How is a business divided during a divorce between spouses?
Average rating 4.5 from 4 users
When divorcing a marriage, spouses are faced with many questions: who will the children stay with, how to divide the property, who will continue to engage in joint business during the divorce, etc. The division of firms and enterprises is an extremely difficult task. In this process, judges have to focus not only on the RF IC, the RF Civil Code and the RF Civil Procedure Code, but also on federal laws. For example, on Federal Law No. 14 on LLCs, Federal Law No. 208 on JSCs, Federal Law No. 74 on peasant farms and other legal and by-laws. Moreover, federal laws can play a primary role in this matter.
What share can a spouse claim if the owner is the husband?
Property that is subject to division upon divorce is determined by Art. 34 RF IC. This includes all property acquired during the marriage. This does not apply only to objects donated and inherited by one of the spouses. But it refers to shares in business, capital, valuable shares.
That is, if one of the spouses or both together have an enterprise or own part of it, then during a divorce they are allowed to divide it. Moreover, it does not matter to whom this business was originally registered. It is possible that the wife had nothing to do with commerce at all, but was only involved in raising children. Russian legislation still establishes the principle of equality of shares in joint property. This means that if the owner of the enterprise is the husband, then the wife should still receive half.
However, dividing a business during a divorce in 2020 is very difficult, if only because equality of shares in this case can lead to a complete stop of the enterprise. The division procedure is even more complicated if the husband founded or acquired a business before marriage, but lived in the family for a sufficient number of years. This section will require serious calculations.
Legal basis for dividing a business during divorce
The joint property regime of spouses is established by Article 34 of the RF IC. Part 2 lists property acquired during marriage, which is regarded as common property. The list includes:
- income received from business activities;
- securities;
- shares in capital.
The listed types of property are the result of doing business. In accordance with the rules of Article 38 of the RF IC, it is subject to division into equal shares.
An important condition is that entrepreneurial activity must be started during the period of marital relations. Otherwise, it is not considered common property and cannot be divided.
Article 36 of the RF IC provides for situations where property cannot be divided . In terms of business, these include:
- receiving property through gratuitous transactions (for example, as a gift or by inheritance of a company);
- starting a business activity before registering a marital relationship;
- opening your own business during marriage using personal funds or property received free of charge.
Despite the simplicity of the criteria by which spouses’ property is recognized as joint, it is difficult to divide a common business. Problems arise when determining the composition of property, correctly assessing its value, and choosing a method of distribution.
How is the business divided between spouses?
The RF IC provides spouses with the right to divide property both on a contractual basis and through the court.
Contract section
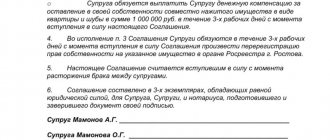
If there is mutual understanding between the husband and wife on the issue of property, then the division of the common property of the spouses can be carried out using a settlement agreement on division. It is concluded both during the existence of the marriage and after the divorce. Spouses can discuss all the nuances, the main thing is that the points of the document do not contradict Russian laws.
Before the wedding or during the marriage, the husband and wife can also sign a marriage contract and establish in it any option for division in any shares.
Both documents must be notarized.
You can view it on our website if necessary.
Judicial division
If it was not possible to reach an agreement during the division of the business, then there is only one way out - to file a claim in court. Each spouse has the right to file a claim. Most likely, when it comes to dividing a business in 2020, the cost of the claim is estimated at more than 50 thousand rubles. Therefore, the magistrate’s court is not suitable, and the application must be filed in a court of general jurisdiction. You should choose the one that is located at the defendant’s place of residence. If this is not possible, then at the location of the enterprise that must be divided.
When making a decision, the judge will be guided by which of the spouses is actually engaged in business and what legal form the divisible enterprise has.
Section methods
In practice, several options are used for the distribution of commercial property between husband and wife. The choice of method depends on the individual situation.
Sale
The simplest solution is to sell the company and divide the money received in equal shares. The share is sold to co-founders or third parties. Features of implementation are established by the statutory documentation. Spouses voluntarily leave the business and receive compensation.
Example 1. Sementsov E.I. and K.N. filed for divorce. During the period of marital relations, Sementsov K.N. opened the company with two co-founders. His share in the authorized capital of the LLC is 33%. The total value of the company's assets is 15,000,000 rubles. In accordance with the charter, the co-founders have the preemptive right to purchase shares in the business. In order to share the results of business activities with Sementsova E.I. the ex-husband sold his share to his partners. The compensation amounted to 5,000,000 rubles. Each spouse received 1/2 of the proceeds - 2,500,000 rubles.
Reorganization
If the company is owned entirely by one or both spouses, then a reorganization is carried out to divide the business. The following options are possible:
- Division - the main company is closed, the assets are divided in half, after which two independent organizations are registered.
- Spin-off - after assessing the assets, a new legal entity is separated from the main company.
This option is suitable for those families in which the husband and wife participate in entrepreneurial activities as equals. The financial interests of both parties will not be infringed. When carrying out the procedure, it is important to record all agreements in writing. It should be clear from the documents that the joint property of the spouses is being divided.
Example 2. After the divorce before Kuznetsova T.A. and ex-husband Kuznetsov D.I. The question arose about dividing the LLC. During the period of marriage, they started a joint business, each of them has 1/2 share in the authorized capital. As a result of the assessment, the market value of the assets was established at RUB 10,000,000. The co-founders decided to divide commercial property and create independent companies. The company's activities were discontinued and its assets were divided equally. Each spouse registered their own company with an asset value of RUB 5,000,000.
Liquidation
If neither spouse intends to continue to engage in entrepreneurial activity, and it is not possible to sell the company, a liquidation procedure is carried out . After the business closes, the assets are divided in half. Real estate, equipment, machinery, inventory become the sole property of the husband and wife. Then individually implemented.
Example 3. Spouses Kosarev Yu.A. and Kosareva N.D. own an auditing firm. After the divorce, running a business together was impossible, so they decided to liquidate the LLC and divide the assets. After the closure of the company, there remained non-residential premises used as an office, profit from business activities in the amount of 1,000,000 rubles. and office equipment. The property was sold for RUB 5,000,000. Office equipment and money were divided in half. The husband and wife received 3,000,000 rubles each. Each of them decided to continue providing accounting consulting services.
Offset with other property
If one spouse is engaged in entrepreneurial activity, and the other does not participate in the business, then the share in the company can be replaced by compensation. The company remains the property of one party, and the other receives property or money.
Example 4. Shvets O.Yu. During the marriage, he opened an LLC and is the sole founder. His wife Shvets I.S. does not participate in her husband's business. After the divorce, the question arose about the division of jointly acquired property. Shvets O.Yu. does not intend to divide the company, he offered his ex-wife compensation for her share in the form of a three-room apartment. The parties entered into an agreement on the division of property. Shvets O.Yu. gave up her share in the company and re-registered the apartment in her name.
Joint management
Few divorcing spouses make the choice to run a joint business. If they do not have personal hostility and mutual claims, they remain business partners. This option is acceptable when the husband and wife take equal part in the activities of the company.
The joint company continues its work, no division is made. The parties agree on the procedure for distributing profits.
Example 5. Spouses Astafieva E.N. and Astafiev D.A. own the company and participate equally in commercial activities. Each of them intends to enter into a new marriage. There are no children together, they are not going to stop business cooperation. When dividing jointly acquired property, they did not divide the business. The procedure for profit distribution was established in the statutory documents.
Options for dividing a company during divorce
It is quite difficult to predict how the business will be divided between spouses. Everything will depend on the form of ownership and the number of participants in the enterprise. If we analyze judicial practice, we can identify the main options that judges adhere to when dividing.
Transfer of rights to the enterprise and monetary compensation
The most common method of division is this: the business becomes the property of one of the spouses, and the other is paid monetary compensation. Its size is established by the court. This is usually half the value of the entire business.
Options for dividing a business when spouses divorce.
The owner becomes the one of the spouses who invested more time and money in the enterprise and manages its current affairs, and also considers it as the main source of income.
Division of one company into several new ones
Business reorganization is more often used if both spouses are engaged in entrepreneurial activities. Otherwise, the idea may turn into the downfall of the entire business. There are several forms of reorganization of a legal entity. If this option is used in a divorce, it is usually in the form of a division into two companies. Less often - in the form of accession or separation. Affiliation is used if one of the parties also has a personal business that is not subject to division, and separation into a branch company is permissible provided that the spouses are ready to cooperate in business in the future.
In any case, when reorganizing, it is necessary to consult a good lawyer throughout the entire process. This form of division is only possible if the entire business belongs entirely to the spouses.
Sale of business and division of proceeds
The sale of business shares is another common form of division between spouses. And perhaps the simplest. The spouses simply sell their assets to interested parties, and divide the proceeds between them in half or in other proportions established by the court.
Liquidation of the company
Closing a company is a long and multi-stage procedure. They resort to it as a last resort: if the spouses decide to completely withdraw from entrepreneurial activity. At least within this structure.
When deciding to take such a step, spouses need to remember that first of all they will have to liquidate all the company’s debts to creditors
What does the division of an individual entrepreneur’s property look like in practice?
Most often, spouses come to a compromise: the property remains safe and sound with the owner, while the other party receives monetary compensation. The spouses evaluate their existing assets and calculate the resulting amount. An entrepreneur who wants to keep his own business can pay his spouse a share in cash. This method of dividing property allows you not to create problems with the enterprise.
If the business includes equipment, transport and other important elements, then it is not advisable to divide these assets - the other spouse does not need the things that are used in the activities of the individual entrepreneur. It’s easier to pay than to take away the property you need. Often both spouses are entrepreneurs with their own businesses. In such a situation, the order of division does not differ from the usual division. Both spouses agree on mutual compensation, and the enterprises remain afloat.
Read: Bankruptcy of an individual entrepreneur: features of the procedure and possible consequences
Features of business division of different organizational and legal forms
Dividing a business can be very difficult. Various organizational and legal forms of enterprises dictate their own methods of division.
Individual entrepreneur
If one of the spouses has the status of an individual entrepreneur, then the property used to conduct business activities is equal to common or personal property. This means that all objects purchased during the marriage for the purpose of running a business will be considered common. Therefore, the court will divide them into two equal parts between the spouses.
Division of shares in LLC
A limited liability company in its activities is subject to the Federal Law on LLC, as well as the Charter of the organization.
In case of divorce, only the division of shares in the authorized capital belonging to the spouses is possible. LLC property cannot be divided during a divorce.
In order for shares in the LLC to continue to generate profit from the operating enterprise, the owner needs the permission of the remaining members of the Company. If it is not given, then only monetary compensation is due.
Be sure to study the company’s statutory documents before the division. Often, in order to insure its assets, a Limited Liability Company has serious restrictions on accepting new members. This means that even if a spouse receives a share in the authorized capital, he still will not be able to enter the business as a partner.
Division of shares in the Joint Stock Company
When dividing a significant block of shares, spouses will definitely need a securities specialist. The main difficulty here is not in determining the shares, but in calculating the value of the shares: exchange, market and nominal. Again, you should study the statutory documents, because JSCs also practice imposing restrictions on the admission of new members. This means that either the shares are sold and the proceeds are divided between the spouses, or the shares go to one of them, and the second receives compensation.
Farming
The peculiarity of the division of a collective farm is that it is divided not on the basis of the RF IC, but on the basis of the law on peasant farms (provided that both spouses are its members). There are two options here:
- The farm ceases operations. The land is divided between spouses based on the Land Code of the Russian Federation. Other property is divided in equal shares or sold and the funds are divided.
- The farm continues to operate, but one member leaves and receives monetary compensation.
What risks does the business bear?
Divorce and division of assets can greatly impact a business. Various types of risks arise:
- reputational due to conflicts between owners or sudden changes in ownership;
- possible conflicts with partners;
- possible conflicts with counterparties;
- depreciation of assets - one of the spouses can artificially reduce the value of the company or encumber their share with collateral.
One of the spouses can re-register the business to third parties, sell or donate it partially or completely without an agreement on the division of property.
The second spouse may try to protect the disputed property, ask the court to seize the property and prohibit the sale of shares and assets (Articles 139-140 of the Civil Procedure Code of the Russian Federation) or recognize the transaction as imaginary and invalid (Article 170 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The applicant spouse must prove the sham of the transaction.
An LLC can be protected by including in the articles of association a provision that a new member cannot acquire a share without the consent of the other members.
Case Study
The ex-wife of Norilsk Nickel co-owner Vladimir Potanin could not receive half of his share in Norilsk Nickel and Interros International Investments Limited in 2014 during a divorce. The court did not recognize the company's shares as the property of the businessman and distributed only real estate and financial assets between the spouses, since beneficial ownership is not regulated by family law.
If one spouse owns a share or all of the assets of the LLC and divides them equally with their partner, this can lead to conflicts in the management of the business, damage the reputation and reduce the value of the business. A conflict between spouses can escalate into a corporate conflict and lead to the dismissal of the team, loss of clients and profits.
It would be appropriate for the contract to stipulate that one of the spouses pays the partner compensation for the market value of assets in exchange for giving up his or her share of the business.
Division of company debts
The division of debts that a company has acquired can take place in two ways:
- The spouse who took out the loan will be considered responsible for the debts. It is possible provided that the spouse spent the money received on personal needs, on his own property, etc.
- Debts are recognized as common, and the spouses will both bear responsibility for them in the future. This option is carried out if the funds were spent on business development or the acquisition of common property of the spouses.
How and what to divide an individual entrepreneur during a divorce
Experts contacted by husband and wife are often required to estimate the value of the business and property owned by the individual entrepreneur in order to help divorcing couples figure out how the individual entrepreneur is divided when the spouses divorce. Tangible assets in a family business include many things. This includes cash, inventory, equipment, and other objects related to the management and activities of small businesses (see Article No. 34 and Article No. 36 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation).
Valuation of individual entrepreneur assets is a subjective process. When dividing the property of an individual entrepreneur during a divorce, each spouse often chooses a separate lawyer to present the argument that will best suit their goals. These experts then present their findings to the court in divorce proceedings.
The judge decides which expert approach is more convincing in a particular situation, unless the spouses have previously agreed on a method that would satisfy both.
What cannot be divided
The RF IC strictly establishes categories of property that are not recognized as jointly acquired property, which means they are not subject to division. First of all, these are objects that became the property of one of the spouses even before marriage, if during their life together no significant improvements were made using funds from the common family budget.
Is it fair to divide a business if only one of the spouses was involved in it?
Not really
Also, a business that was inherited by only one in a married couple or became property under a gift agreement will not be divided.
Also, parents do not have the right to divide parts of the business that belong to their minor children.
How to divide business debts
Debts from business activities can be recognized as both general debts and debts of the businessman spouse. It all depends on what purposes the business income was spent on and whether it went into the general budget.
If the business is divided between spouses, then the debts are subject to division in proportion to the established shares (Article 39 of the RF IC).
According to Art. 2 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, entrepreneurial activity is an independent activity that is carried out at one’s own risk by a person who is registered in this capacity in the manner prescribed by the legislator.
Therefore, if the income from the business was not received by the family and was not spent on the purchase of common property, no one will divide it between the spouses.
Arbitrage practice
An analysis of judicial practice shows that small and, less often, medium-sized enterprises are usually divided through the courts in Russia.
If we are talking about the division of large corporations, then their owners try to stipulate all issues in advance in marriage contracts or resolve the issue behind closed doors with the involvement of their lawyers and without public interference. To avoid undermining trust in the company. Carrying out the division of a business during a divorce in 2020 is not an easy task. In this matter, judges have to focus on a large number of federal regulations and the organizational form of the enterprise itself.
Section order
The results of business activities can be divided by agreement of the parties. If disagreements arise, you must go to court.
Before the divorce
Spouses have the right to take care of the fate of the business before registering the marriage and during the marital relationship. To do this, a marriage contract is drawn up, which stipulates the conditions for the distribution of property after a divorce.
To draw up a contract, it is recommended to seek the help of a family lawyer. After signing the document, it is certified by a notary.
By agreement of the parties
If a prenuptial agreement has not been drawn up, the husband and wife can come to an agreement during the divorce process. To ensure a fair distribution of property, you must seek the services of an independent appraiser.
During negotiations, the spouses determine:
- what will become the personal property of the spouses;
- what property will be divided.
The division may be made in unequal shares. At the same time, the financial interests of the other party should not be infringed.
Once an agreement is reached, a separation agreement is drawn up. The legislator does not provide for mandatory notarization of a document. To avoid disagreements, it is advisable to seek the services of a notary.
Through the court
Often spouses cannot come to an agreement, so they are forced to go to court.
The plaintiff must take the following actions:
- draw up a list of property, securities, describe the general business;
- collect documentation confirming ownership, property value, date of registration of an individual entrepreneur or company;
- draw up a claim and submit it to court;
- justify your position during the trial;
- receive a court decision and wait for it to come into force.
If the defendant does not want to execute the judicial act voluntarily, he should contact a bailiff.
How is an individual entrepreneur divided through the court upon divorce?
There are several scenarios that can typically arise during the legal division of business and property in a divorce:
- Most often: the individual entrepreneur and all his property is divided in half, since it is jointly acquired property (see RF IC, Article 39).
- It happens: a judge can decide (by agreement of the parties) that the individual entrepreneur and all his property should be left to the spouse with greater involvement, and the other spouse will receive compensation.
- Sometimes: the court may order the sale of the individual entrepreneur and all his property, and divide the proceeds (by agreement of the parties).
- Rare: The business is still jointly managed by both parties (by agreement of the parties).
To resolve controversial issues of the IP section, the plaintiff applies to the district court at the place of registration. When the judge makes a decision, having received a copy of it, you will need to present it to the bailiffs to open enforcement proceedings.
Terms of division of property
When dividing the property of an individual entrepreneur, a standard three-year statute of limitations applies (Article 38 of the RF IC), defined for all cases related to the division of property of spouses.
After filing a claim, the judge must make a ruling on it within five days. If it is accepted for proceedings, the judge is obliged to consider the claim within the next two months. In practice, such cases are delayed for six months due to the filing of petitions and the periodic absence of the parties at court hearings, etc.
To divide the property of an individual entrepreneur, spouses have the right to use the contractual method by drawing up an agreement and distributing the property in any convenient shares. If there are disputes, the parties can make a division in court.