The rights and responsibilities of heirs are what make them heirs from a legal point of view. In general, lawyers tend to view people as a set of rights and obligations. If you are a deputy, then you are nothing more than a set of rights and responsibilities to pass laws, persecute homosexuals and curse the West. Just a joke, of course. Everything is somewhat more complicated.
Right is the ability to do as you want. Of course, within the law.
A duty is something you must fulfill by law. And if you can dispose of your rights as you please (use them or forget them), then you must certainly fulfill your duties.
That's it with introductions, let's look at the specific rights and responsibilities of heirs.
Inheritance of debt obligations
Content
First you need to understand what inheritance is. Inheritance is understood as the totality of the assets and liabilities of the deceased (Article 1110 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The hereditary mass is formed as a single whole; it is impossible to separate a certain part from it and discard the rest (Article 1158 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Debts are included in the inheritance along with the property of the deceased. Thus, the inheritance consists of all the property that was owned by the deceased at the time of his death, and all his debts (Article 1175 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
During the inheritance process, only the property of the deceased is subject to division. After which, each legal successor who has registered the rights to the inheritance receives a share of the debts proportional to the share of the property received.
Example. Ivan was the owner of an apartment and a car. He also had a loan. At the time of his death, the loan balance was RUB 400,000. When dividing the inheritance, his wife, child, mother and father each received a ¼ share in the property. That is, ¼ share of an apartment, a car and 100,000 loan debt.
Inheritance protection
The body that acts to protect the property rights of both the testator and heirs is the notary (federal law “On Notaries ...”).
Actions of the notary for protection:
- notifying all possible heirs about the fact of opening an inheritance.
- Issuance of certificates after completion of the property distribution procedure.
- Recognition of a will as valid or invalid.
- Protection of inherited property.
- Accepting applications for property ownership from heirs.
- Establishing a period after which the property can become the property of a new person.
- Conclusion of an agreement on the rights to manage property (enterprise).
- Checking all documents to determine their authenticity.
Important! In addition, the property rights of heirs are protected by the Civil Code (Chapter 62). It determines the shares of property for each heir, the order of transfer of these rights, and protects the rights of the disabled and minor dependents. It also prescribes cases in which the heirs are considered unworthy or the will is declared illegal.
Liability for the debts of the testator
Debt obligations pass to the heirs, regardless of whether they received the right to property by will, by law, by inheritance agreement, or as an obligatory share.
Beneficiaries under a testamentary refusal or testamentary assignment do not inherit the debts of the deceased.
Obligations that are inherited
However, in accordance with the law, not all debts are transferred to legal successors. Heirs are liable only for property obligations. That is, they must pay:
- loans;
- loans from individuals;
- debts collected through the court and being executed by bailiffs.
In this case, obligations not related to the personality of the deceased are not transferred to the heirs. These are alimony, fines, obligations to perform certain actions.
Note! The same debt can be inherited or not. For example, if a fine was issued to a deceased person, then it is not included in the inheritance. And if it has already been collected through the court, then it goes over.
Separately, it is necessary to highlight the debt for alimony. After the death of the payer, the obligation to pay alimony ceases. But the alimony debt and the penalty are included in the inheritance. In accordance with the Ruling of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation in case No. 18-КГ18-267 dated February 26, 2019, the amount of debt for the heir is calculated taking into account the statute of limitations rules. Since alimony must be paid monthly, the statute of limitations is calculated separately for each payment. That is, all payments that the deceased should have made more than 3 years ago and the penalty for them must be excluded from the inheritance.
Mortgage
Inheriting a mortgage is a different story. This is not just a loan, it is secured by collateral.
The peculiarities of inheriting a mortgage loan are that the apartment is divided independently, and the loan balance is divided independently.
Procedure for dividing an apartment:
- when inheriting under a will, the apartment is divided in shares provided by the testator;
- in case of inheritance by law, the apartment is divided in equal shares among all heirs;
- citizens who lived in the apartment at the time of the death of the testator have a priority right to receive a share in the apartment as an inheritance.
In this case, the debt is divided as follows:
- if the spouse is a co-borrower, then the debt goes to the spouse in full;
- when inheriting by law, the debt is divided between the heirs in equal shares, even if one of the heirs did not receive ownership of a share in the apartment;
- when inheriting by will, the debt is divided among all heirs, in proportion to the shares in the inherited property.
Limitation of liability of heirs
In simple words and using the example of a user, the value of the property that the user inherited is 500,000 rubles (1,500,000 / 3), and the total amount of debts is 950,000 rubles. Based on the additional condition: “within the cost”, it follows that more than 500,000 rubles cannot be recovered from him.
However, property by inheritance passes into shared ownership, which means that debts also pass into shared ownership. And based on the size of the debt of 950,000 and 1/3 of the inheritance, the user will only have to pay approximately 317 thousand rubles.
However, in the rules of inheritance there is a second additional condition:
Limitation period for debts of the testator
The debts of the deceased are subject to the general statute of limitations (Article 196 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). It is 3 years. The period begins to run from the moment the creditor learned of the violation of his rights.
Example. Alexander took out a mortgage for the apartment. The man received an unstable salary, so he kept money in his mortgage account to pay loan installments for 3 months in advance. After his death, the loan installments were written off on time for another 3 months. When the money in the account ran out, the bank began to look for the debtor. Having found out that he had died and his heirs lived in the apartment, the bank addressed its demands to them.
If creditors have not turned to a notary or heirs to collect the debts of the deceased within 3 years from the date of his death, then it will not be possible to collect the debt through the court.
Often, heirs, when accepting property, rely on the statute of limitations. They hope that the creditor will not find out about the death of the deceased and the deadlines will expire.
But, as practice shows, creditors deliberately wait a long time before presenting claims so that the heirs can assume their rights. Since often, upon learning about the debts, the successor refuses to accept the inheritance.
Inheritance with debts
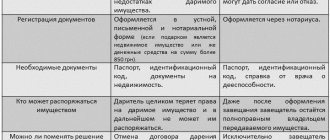
One of the features of entry after the death of the testator is the transfer to the receivers, along with the inheritance mass and the debt obligations of the deceased. You cannot refuse to receive debts.
Before entering into an inheritance with debts, the receiver can decide whether to accept such property or not. If there is no desire to receive the encumbrance, for example, due to the large debt of the deceased, then the recipient can issue a refusal to join.
Partial acceptance of the testator's possessions is impossible. You cannot inherit an apartment and give up your car and debt obligations. When registering the receipt of the property of the testator, debt liability is also transferred to the incoming receiver. Only heirs who have not shown interest in inheriting within the specified time frame or have refused this opportunity are exempt from it.
Read our articles about registration and deadlines for applying to a notary.
Is it possible not to answer for the debts of the deceased?
As follows from paragraph 60 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation of 2012, liability for the debts of the testator is borne by all heirs who accepted the inheritance, regardless of the basis of inheritance and the method of accepting the inheritance.
If the heir formalized the property of the deceased or actually accepted it, then he is obliged to pay his debts. However, the law provides several ways to avoid liability for the obligations of the testator.
Among them:
- refusal of inheritance;
- payment of debt in an amount not exceeding the amount of property;
- waiver of personal debts of the deceased.
Let's take a closer look.
Refusal of inheritance
The debt of the deceased cannot be collected from the heir if he refused to enter into the inheritance. However, the law provides for several types of refusal:
- by default – the heir does not visit the notary’s office and does not accept the property of the deceased;
- through a notary - writes a corresponding application and pays the state fee.
If the deceased had large debts, then it is advisable to formalize the refusal in notarial form. This will help avoid negative consequences.
If the creditor goes to court to recognize the heirs as having actually accepted the inheritance, then the court will interpret any actions of the heirs in favor of the plaintiff.
Example. Ilya and Yegor did not accept the inheritance after their father’s death. The deceased owned an old house and a small plot of land. The brothers came several times, inspected the property and decided not to register the inheritance. However, the testator owed the bank a large sum. And the creditor went to court to recognize Yegor and Ilya as having actually accepted the inheritance. Since the neighbors saw that the men visited the site several times, the court satisfied the applicant's demands. But the mother of the deceased did not visit the site, and therefore was not recognized as accepting the inheritance.
The problem with Ilya and Yegor was that the men did not formalize a written refusal of the inheritance. If there was a document, the court would take their side.
Information about the debts of the deceased may not appear immediately. Therefore, the law provides for the heir the opportunity to refuse the inheritance after its acceptance until the expiration of 6 months from the date of death of the owner. That is, the heirs can issue a written refusal before receiving a certificate of inheritance rights, even if they have already submitted an application to the notary to accept the inheritance.
Limits of liability of heirs
In accordance with Art. 1175 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, heirs are liable for obligations exclusively within the limits of the property received. That is, the successor cannot collect the debt from them in full if it exceeds the amount of the inherited property.
Therefore, it is not profitable for legal successors to enter into an inheritance if the deceased has large debts. Registration of property requires significant financial costs and no one will reimburse their heirs.
Personal debts of the deceased
Separately, it is necessary to highlight the situation with inheritance by a spouse. All property that a husband and wife acquire during marriage is considered joint property. Each of them has the right to ½ share, regardless of who the specific object is registered to. Therefore, in the event of the death of the deceased debtor, creditors have the right to demand repayment of the debts of the testator, including at the expense of his share in the joint property.
In this situation, it does not matter whether the spouse accepted the inheritance or not. Moreover, if the surviving spouse does not promptly contact a notary to allocate the marital share in the joint property, then his share may also be used to pay off debts.
In addition, creditors can go to court and collect the remaining debt from the spouse, since debts in marriage are also common. The only option to avoid payment may be to prepare evidence that the deceased took out loans for personal needs. For example, for your own treatment, for purchasing personal items.
Payment of the deceased spouse's obligations can be avoided with a prenuptial agreement. If the document provides for a separate property regime, then debts cannot be collected from the deceased’s spouse.
Who can I ask about the encumbrance?
You can find out whether the deceased heir has debts on the transferred property by asking a notary about it. Creditors, if there are debts left unpaid by the testator, transfer this information to the notary.
Sometimes it may happen that the information will not be transferred to the notary, but will be transferred in a statement of claim to the court .
Information about estate debts may influence the decision to accept or reject a proposed inheritance.
What should the testator's creditors do?
The testator's creditors can be not only banks, but also private individuals. And they also have the right to receive debt from the inherited property.
To do this you need:
- Prepare evidence of debt transfer.
- Prepare a claim.
- Go to court.
- Get a court decision.
- Submit the decision to the bailiffs.
To collect a debt from a deceased person's estate, the creditor must prepare evidence that the money was transferred. In this situation, indisputable evidence is a notarized loan agreement and a receipt for the transfer of funds.
The fact of proof rests with the plaintiff, so it is the creditor who must prove that the funds were transferred.
The nuances of collecting debt from heirs:
- The loan agreement must be drawn up in writing; certification by a notary is welcome.
- The agreement must contain the full name, passport details and place of registration of the parties.
- The fact of transfer of funds must be confirmed by a receipt drawn up by the deceased, or an extract from the plaintiff’s bank account confirming the transfer of funds.
- All heirs who have acquired rights are indicated as defendants.
- The loan agreement can be drawn up either in written or printed form.
- Signatures of the parties are put in their own hands.
- The date of conclusion of the contract must be indicated.
- Failure to decipher a signature is not grounds for refusal to reimburse a debt.
Note! If the heirs wish to invalidate the loan agreement, then they must provide evidence. A mere request for a handwriting examination is not enough. Along with it, the heirs must provide free samples of the deceased’s handwriting.
Claim against heirs for debts of the testator
The statement of claim to the heirs of the deceased must contain:
- name of the district court at the place of residence of the heirs;
- creditor details;
- information about the defendants;
- amount of claim;
- amount of state duty;
- name of the claim;
- information about the death of the debtor;
- information about the entry of heirs into rights;
- loan information;
- information about receipts;
- reference to law;
- claims for debt collection from heirs;
- list of documents;
- date and signature of the applicant.
Sample claim
What is not included in the inheritance
You might be interested in:
Inheritance law
What is and how is renunciation of inheritance regulated in Ukraine?
Read more
Inheritance law
What to do if the notary is in no hurry to issue a certificate of inheritance
Read more
Inheritance law
Division of inheritance in Ukraine
Read more
Inheritance law
Lifetime inheritable ownership of land
Read more
Inheritance law
Secret will: aspects of application
Read more
Inheritance law
How much will it cost to register a will in Ukraine?
Read more
The heir cannot receive obligations that are related to the personality of the deceased:
- obligations to pay alimony;
- the need to compensate for moral damage or harm caused to the health of a third party;
- fines.
The heirs are not obliged to repay the debts of the deceased that are not supported by documents: receipts, agreements, and other documents. Verbal agreements most often remain unsatisfied.
Arbitrage practice
Judicial practice regarding the debts of the testator is very extensive. Creditors do not always request debt from heirs in accordance with the law.
Popular violations of the rights of heirs are:
- Requirements for payment of the full amount of the debt. The heir is liable only to the extent of the property received.
- Filing claims against one heir. Legal successors must fulfill obligations in shares equal to the shares of the received property.
- Requirement to pay a debt before the expiration of the contract. The death of the borrower is not a basis for early fulfillment of obligations. Therefore, the creditor cannot collect the debt from the heirs if the contract has not yet expired.
- Minors and incapacitated heirs receive a share of the debt equal to the property received, like other legal successors. Their debt is satisfied from the inheritance received and cannot be recovered from the parent or guardian.
Lawyer's answers to private questions
After the death of the spouse, she applied for the allocation of the marital share. After which she accepted the inheritance along with his parents. After receiving the certificate, it turned out that the husband had a large loan. Am I responsible for his debts only within the framework of the inheritance or through the marital share too?
The heirs are liable for debts within the inheritance. But if the creditors go to court and prove that the money was spent in the interests of the family, then recovery can be applied to the marital share. However, lenders must prove that the loan was spent on the family.
My husband had a privatized apartment. It lists 2 common sons. Now he is dead. A loan of 80,000 rubles was issued for him. Can I not accept an inheritance so as not to pay the loan?
Please check in advance whether the loan has been insured. If you have insurance, you will be able to get a share in the apartment and repay the loan. If there is no insurance, then you have the right not to accept the inheritance and not pay the debt.
The ex-husband had several debts under writs of execution. If he dies, will the debt go to the children? Is it possible to release them from debt if they are 2 and 5 years old?
If you, as a representative of the children, formalize an inheritance in favor of the children, the debt will also pass to them. Being a minor is not a basis for exemption from debt.
My father was a guarantor for a loan from a friend. A friend stopped paying his loan. The bank went to court to collect the debt jointly and severally. But the father died. Will this debt be passed on to the children?
The debt will pass to the children. But they have the right to pay it and collect this amount by way of recourse from the borrower.
My mother gave me an apartment in her will. But she established the condition that her stepfather live in the apartment for life. In addition to the apartment, she had loan debt. Will this debt be divided between my stepfather and I, or will it go entirely to me?
The beneficiary of a will does not receive a share in the debt. Since the property of the deceased is the property of the heirs.