Home/Division of property/Determination of jurisdiction
When declaring or challenging their rights to common property, spouses must not only correctly prepare a statement of claim, but also submit a petition for consideration to the appropriate government body. This does not mean that for the presentation of documents for the division of property during the divorce of a married couple, any court is chosen, which is closer to home or according to other criteria. Each government agency has its own jurisdiction over civil cases. In order to find out which court the spouses need to contact when dividing property upon divorce, it is worth reading this article.
Attention! If you have any questions, you can chat for free with a lawyer at the bottom of the screen or call Moscow; Saint Petersburg; Free call for all of Russia.
Normative base
When resolving issues related to property disputes between married couples, it is worth paying attention to the following legal documents:
- To determine the competence of the court regarding the division of property during a divorce, it is worth turning to the Civil Procedure Code of Russia, namely Chapter 3. It regulates the jurisdiction of government agencies. The concept of exclusive jurisdiction has also been defined, which also occurs when dividing real estate between spouses during divorce.
- The Family Code of our country also regulates the property issues of husband and wife. In particular, Chapter 7 distinguishes between the concepts of common and personal property, and also determines the size of shares when dividing real estate.
- The Civil Code of Russia in Section II defines the concept of “ownership right”, considers issues related to its acquisition, and also regulates the conditions and circumstances when the termination of this right occurs.
- The Russian Tax Code specifies the amount of the state duty, which is paid when filing a claim with a judicial authority.
What is the jurisdiction of cases on division of property during divorce?
When deciding to begin distributing acquired property, a husband and wife must first understand which court will hear the case. When determining jurisdiction for the division of property during a divorce, some points should be taken into account:
- property will be divided during the divorce process or separately;
- what is the total size of the property in monetary terms (assess the value of the property);
- Is there real estate among the divisible things?
It is from the resolution of the above issues that the state judicial body is determined, which is competent to consider cases of division of property of married couples upon divorce.
In this regard, tribal and territorial jurisdiction are distinguished when dividing property during a divorce. Generic is the competence of courts at different levels of the judicial system. In our country, magistrate and district courts deal with claims regarding the division of common property of spouses.
IMPORTANT
It is also important to determine the territorial jurisdiction of the government agency for the division of property upon divorce. After all, by filing a claim at the wrong address, the resolution of property issues may drag on for a longer period. Thus, federal courts are divided into territories according to city districts. Magistrates' courts are divided into sections. In each individual subject of the Russian Federation there is a certain number of such courts, depending on the number of population in a given territory.
An application for division of joint property during divorce is submitted:
- At the place of registration or location of the defendant (Article 28 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation);
- At the address of the location of the real estate (clause 1 of article 29, article 30 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation);
- According to the territory of residence of the plaintiff, if the consideration of disputes about property is resolved in the same proceedings with the case on the termination of marriage, in accordance with paragraph 4 of Article 29 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation and Article 31.
Spouses (parties to the case) have the right, by mutual consent, to change the jurisdiction at the place of consideration of their case before it is accepted for proceedings, with the exception of resolving issues of division of real estate ( Article 32 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
Property safety
Magistrates' Court Often spouses take out expensive items on credit, such as real estate or cars. And they do not always pay off the entire debt before the divorce. In such a situation, the debt is usually divided equally. But a different solution can be achieved if appropriate evidence is provided. Moreover, if you prove that only the defendant used the property purchased on credit, and the debt was paid from the family budget, you can additionally demand compensation for half of all payments made. But in such a situation, you will have to give up the idea of getting the said property.
Major renovation of an apartment in the eyes of the court is joint property
How to determine jurisdiction when dividing property?
To file a claim for division of property during a divorce, you need to determine directly to which court the documents should be sent.
Attention
The consideration of civil cases regarding the division of property during divorce is handled by the magistrate and district courts. The competence of the bodies is determined by the articles of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation. According to the law, the magistrate court hears cases on property issues, the value of which does not exceed 50,000 rubles. Anything more than this amount is already under the jurisdiction of the district authority. At the same time, the amount of the claim should be understood as not just an estimate of the price of the divisible property. The determination of the amount also includes interest, fines, penalties, penalties for contractual legal relations (for example, those specified in the marriage contract). The price of the claim is determined by the amount claimed by the applicant (i.e. ½ of the total assessed value).
When determining jurisdiction, when considering in one claim not only the issues related to the division of general welfare, but also the issue of children in a divorce (where and with whom they will live, the order of meetings with the parent, etc.), this category of cases also is under the jurisdiction of the district court, regardless of the cost of the required material assets (Article 23 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
What is territorial jurisdiction when dividing property in a divorce?
Territorial jurisdiction for the division of property of spouses during a divorce implies the determination of the government agency whose competence is to consider the case, according to location. Jurisdiction is determined by the Code of Civil Procedure of Russia and cannot be violated. Thus, district courts are divided according to the number of districts in the city; peace settlements - to court districts; their number is determined by the size and density of the population of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
You can file a claim for division of property during a divorce:
- At the place of residence of the defendant (main jurisdiction, Article 28 of the Code of Civil Procedure);
- At the location of the property (exclusive jurisdiction, paragraph 1 of Article 29, Article 30 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation);
- At the choice of the plaintiff (alternative, paragraph 1 of Article 29 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation)
- At the plaintiff’s place of residence (if it is physically impossible to bring a claim and attend court hearings at another address and if there are minor children, paragraph 4 of Article 29 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
- At the choice of the parties (negotiable, Article 32 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
How is jointly acquired property divided?
According to the provisions of Art. 39 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation, property that was acquired by spouses during a marriage relationship belongs to the latter on an equal basis and, accordingly, is divided according to the same principle.
However, courts still deviate from the principle of equality when dividing common property between spouses under the following circumstances:
- A minor child or children live with one of the spouses, in whose interests the court increases the share of the common property for such spouse .
- The court may reduce the share of one of the spouses when dividing property if the latter acted contrary to the interests of the family in terms of waste of family property, and also for unjustified reasons did not contribute to family well-being.
- The share of a husband or wife's property may be increased due to the illness or incapacity of one of them.
- Also, a much smaller part of the jointly acquired property will be received by the spouse who abused alcohol, was wasteful, and also committed other actions that carry signs of immoral behavior.
Which courts hear cases regarding the division of joint property of spouses?
In accordance with the articles of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, proceedings in property disputes between spouses are under the jurisdiction of the magistrate and district courts. The main difference is the amount of the claim. According to the law, the magistrate court considers property disputes worth no more than 50 thousand rubles, and district courts - over this amount. In addition, it takes into account the fact that a claim for the division of property of spouses during a divorce is considered separately or together with demands for payment of alimony, determination of the place of residence of children, the procedure for communication with offspring, etc.
What property do spouses share?
After citizens have decided to change the regime of joint property of spouses, the question arises as to whether any property can be divided?
Civil legislation contains a number of restrictions that must be taken into account when dividing property between spouses. You can understand these nuances with the help of a specialist in the field of family law, who will explain in detail the requirements of the law at a legal consultation .
Property subject to division between spouses
The regime of joint property of spouses applies to the following property acquired by citizens during marriage:
- income from labor or business activities;
- various cash payments, including pensions, compensation and benefits;
- movable and immovable objects;
- securities, various savings, shares and bank deposits;
- shares in the capital of commercial organizations;
- income from intellectual activity.
The above property can be used jointly by citizens and, if there is an intention of the parties, is subject to division both during marriage and in the event of divorce. If a dispute arises about the division of property of the spouses, the right to demand the due share may, among other things, be a citizen who did not work during the period of family relations and was engaged in housekeeping, or who could not engage in labor activity for health reasons.
What property is not subject to division?
It is important to remember that not all property acquired by spouses during marriage is subject to division. For example, items such as clothes, shoes or school supplies purchased for children must be given to the parent with whom the children live. If a bank deposit was opened in the name of a minor child and funds were deposited into it, then such property will not be included in the requirements for the division of property of the spouses.
Moreover, some things belong to each spouse separately, regardless of whether the property was divided or not. Thus, the list of objects that spouses own and dispose of separately throughout the entire period of the marriage relationship includes:
- personal items (this could be clothing, shoes, etc.);
- the rights of the author in the event that a citizen has created an object of intellectual property;
- property acquired before marriage registration;
- objects received as a result of inheritance or gift.
This property is not subject to the regime of joint ownership, therefore, it is also not subject to division between spouses.
Division of spouses' property in the magistrate's court
Magistrates' courts hear cases of division of property, the amount of the claim does not exceed 50,000 rubles (article of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation). The application may be refused, or the petition may be redirected to the district court if, in addition to a property dispute, the plaintiff raises an issue that is not within the jurisdiction of the magistrate’s court (for example, disputes about children).
For your information
The cost of the claim when dividing the property of the spouses consists of all material claims specified in the application. At the same time, the financial value of the property must be real, taking into account the market value and percentage of depreciation. If the judge has doubts about the required and actual price of the property, the government representative has the right to give his assessment of the divisible property.
If the defendant proves that the property has a higher price than the plaintiff indicated, the magistrate has the right to redirect the case to the district court (if the value of the claim has become over 50,000 rubles) (Article 33 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation). The cost of the statement of claim is determined by the amount of material assets claimed, and not by their total value (clause 1 of Article 91 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
A claim for the division of property of spouses has a three-year statute of limitations from the moment of violation of property rights (Article 38 of the RF IC).
When filing an application with the court, the plaintiff must pay a state fee. Its amount depends on the price of the claim and is regulated by the Tax Code (subclause 1. clause 1 of article 333.19 of the Tax Code).
Division of disputed property through court
The presence of disputes, i.e., the spouses’ disagreement with the procedure on a voluntary basis, determines the further procedure of division through the court. In particular, you will have to go to court in the following cases:
- it is not possible to determine the composition of the common property;
- disagreements regarding the determination of shares in joint property;
- disputes about the division of property that is not subject to division, except for cases where the joint contribution of the spouses has led to an increase in the value of the property.
The basis for division is an application submitted to the court. This is possible both before termination, during or after.
Statute of limitations
According to the RF IC, a three-year statute of limitations applies to demands for division. Based on Art. 200 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the period begins from the moment when the citizen learned about the violation of his rights.
Even if at the time of the divorce the spouse knew about the existence of his share in the apartment, but did not plan to dispose of it, being confident that it already belonged to him, but subsequently the other party refused to transfer it into disposal, the countdown does not begin from the date of divorce , but from the day of receipt of the refusal.
Jurisdiction of cases on division of property
Based on Art. 23 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation in the presence of disputes about division and the value of the claim is up to 50,000 rubles. should go to the Magistrates' Court. In other cases, documents are submitted to the district judicial authority.
Territorial jurisdiction A claim for division is filed at the location of the dividing property, if we are talking about land plots, enterprises, real estate (Article 30 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
For the division of a bank account, the claim is sent to the defendant’s residential address. In case of combined requirements for the division of an account and real estate, you should contact the address of the location of the objects.
In the district court, division cases are considered for no more than 2 months. In the magistrate's court, the period is reduced to 1 month.
Step by step section procedure
The division procedure in the event of disputes through the court is carried out taking into account the following nuances:
- Determination of the composition of common property. This is reflected in the claim filed by the plaintiff. The defendant has the right to file an objection to the claim, indicating specific property that is not to be included. The final decision on the composition is made by the court, having considered the arguments of both parties.
- Conducting an assessment. The examination is carried out before the filing of a claim by the initiator or during legal proceedings at the request of one of the parties to conduct a forensic examination. On its basis, the value of the property is established, and shares in it are determined by the court. If the price of the share of an item for one party exceeds the value of the allocated part of the other, the difference is paid in the form of compensation.
- Percentage of shares. By default, the property is divided in half. You can apply for an increase in share on the basis of Art. 39 of the RF IC, if a child remains with the spouse, the other party did not work during their cohabitation for good reasons or spent money to the detriment of the interests of the family.
The partition process looks like this step by step:
- The plaintiff determines the composition of the common property and reflects it in the claim. The defendant receives a copy of the application and, if there are objections, sends a response to the court, indicating which property cannot be considered common. It is also possible to file an objection at a court hearing. The court takes into account the dates of acquisition of property, circumstances and other factors influencing the allocation of shares.
- The claim is filed in court according to established rules.
- The judge makes a ruling on the start of proceedings and notifies all parties involved.
- On the appointed date, the initiator and the defendant appear at the meeting and present evidence of their case regarding the division and determination of shares.
- The court makes a reasoned decision no later than 2 months from the date of acceptance of the application.
- The decision takes effect after a month. This time is given to the parties to appeal.
If there are disputes between the parties about property and shares in it, they can only be resolved by the court. This also includes incorrect determination of the composition of joint property if the defendant filed an objection to the claim.
Property valuation
Valuation of disputed objects is a mandatory stage, without which it will not be possible to fairly and fully divide the common property.
Table “Principles and stages of division of material goods”
| Nuances | Peculiarities |
| Who attracts | There are no uniform requirements for who should initiate the assessment of joint property. The law does not prohibit the simultaneous carrying out of the procedure by both spouses. The couple can separately invite specialists in order to prevent dishonest assessment to reduce the share of the other party. The plaintiff/defendant has the right to file a motion during the consideration of the claim with a request to schedule a re-examination if there is no confidence in the results presented by the second partner. |
| Who conducts | The assessment can be carried out by private or government organizations that have the appropriate license. |
| Calculation rules | The legislation establishes uniform indicators on the basis of which the state duty is calculated when dividing real estate:
|
Required documents
When applying to a judicial authority, the plaintiff provides:
- Statement of claim,
- receipt of transfer of state duty,
- passport,
- marriage and divorce registration certificate,
You will also need documents for dividing property:
| Bank accounts | Certificate from a financial institution |
| Real estate | Extract from the Unified State Register, registration certificate, certificate from the BTI, expert opinion on the cost |
| Automobile | PTS, STS, purchase and sale agreement |
Payment of state duty
Initially, the plaintiff pays the fee. Subsequently, it can be distributed between the parties in proportion to the awarded shares upon the initiator’s application for compensation of legal expenses.
According to Art. 333.19 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the amount of the duty depends on the value of the claim:
| Up to 20,000 rub. | 4%, minimum 400 rub. |
| From 20 to 100 thousand rubles. | 3 %+800 |
| From 100 to 200 thousand rubles. | 2 %+3200 |
| From 200 thousand rubles. up to 1,000,000 rub. | 1 %+5200 |
| From 1,000,000 rub. | 0.5%+13,200, maximum 60,000 rub. |
Certain categories of citizens receive benefits when going to court and are exempt from paying fees (Article 333.35 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). These include:
- heroes of the USSR or the Russian Federation;
- full holders of the Order of Glory;
- veterans and disabled people of the Great Patriotic War;
- former concentration camp prisoners.
The right to benefits is confirmed by certificates or certificates from authorities.
Based on Art. 64 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the court may grant a deferment or installment plan for the payment of the duty due to the difficult financial situation of the plaintiff or defendant. To do this, an application is submitted to the judicial authority citing difficult circumstances. Attached to it are certificates of earnings or registration with the Employment Center as an unemployed person.
Contents of the statement of claim
The claim is filed in accordance with Art. 131 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation and must include the following data:
- Full name, date of birth of the parties to the proceedings;
- dates of registration and divorce;
- name of the judicial authority;
- an inventory of common property along with technical data;
- a requirement for division indicating specific shares or amounts of compensation;
- a list of the attached documentation;
- plaintiff's signature.
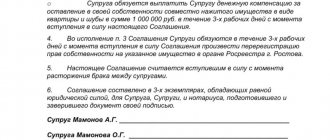
Sample statement of claim for division of property
To the Central District Court of Arkhangelsk
Plaintiff: Efimova O.N.
Address: Arkhangelsk, st. Mirnaya, 28.
Defendant: Efimov K.L.
Address: 620576 Arkhangelsk, st. Zavodskaya, 7, apt. 57.
Statement of claim for division of property
A marriage was registered between me and the defendant Efimov K.L. on May 20, 2015 at the Central Civil Registry Office in Arkhangelsk.
On July 17, 2018, our marriage was dissolved on the basis of a joint application to the registry office, registration act No. 57350. Before the divorce, the division of common property was not carried out. There was no agreement or prenuptial agreement.
During the marriage we acquired:
- Apartment at the address: Arkhangelsk, st. Zavodskaya, 7, apt. 57. Total area – 52 sq.m. estimated cost – 3,500,000 rubles, number of rooms – 2.
- Toyota car, Corolla model, 2020, silver color, VIN number w67302kg57303, license plate K583ER, 77 reg. Estimated cost – 1,000,000 rubles.
The total price of the property is RUB 4,500,000.
According to Art. 38 of the RF IC, common valuables are divided in equal shares between spouses. I believe that ½ share in the apartment should be transferred to my ownership, since I live in it and have no other place of residence, and the defendant must also compensate me for half the cost of the car.
The defendant's property should be transferred to ½ share in the real estate and the car after payment of compensation to me.
Based on the above, I request:
- Recognize shares in common property as equal.
- Divide the common property, allocating the plaintiff ½ share in the common apartment.
- To recover 500,000 rubles from the defendant in favor of the plaintiff. as compensation for the share of the car.
DateSignature
Arbitrage practice
More often, division cases are resolved without problems and the courts manage to divide property according to the law; subsequently, decisions are rarely challenged. Problems arise when dividing real estate acquired by a spouse as an inheritance, if during the marriage its market value was increased at the expense of common finances.
Let's look at a practical example:
The man inherited an apartment with an area of 57 square meters from his father. At the time of inheritance, its value was 1,000,000 rubles. The low price was due to the poor state of repairs and life support systems. Together with his wife, he made a major overhaul, changed pipes and radiators, and carried out a partial reconstruction. The total investment amounted to 2,000,000 rubles.
In 2020, a woman filed a lawsuit for divorce and division of property, including the apartment inherited by her husband. The defendant did not agree with the requirements, filed an objection and indicated that property received as an inheritance was not subject to division.
The plaintiff did not agree with the arguments, citing Art. 37 of the RF IC, according to which property, the value of which was increased during the marriage, is recognized as common property. She provided receipts for expenses and the expert report.
Having considered the arguments, the court included the inherited apartment in the mass of common property.
Division of property of spouses in the district court
The division of spouses' property in a district court is regulated by Article 24 of the Code of Civil Procedure of Russia. According to the law, this government agency has jurisdiction over cases of general jurisdiction that are not subject to other courts. Based on this, consideration of property claims by the district court occurs when the cost of all claims starts from 50,000 rubles.
If the application, along with the division of property of the spouses, raises the issue of children, then this dispute is also under the jurisdiction of the district court, regardless of the amount of the claims.
After determining jurisdiction over the division of property during a divorce, and before submitting documents to the district court, as well as to the magistrate's court, it is necessary to pay a state fee. The fee is calculated based on the value of the property claims of the husband and wife, according to paragraph 1. Clause 1 of Article 333.19 of the Tax Code. The receipt must be attached to the documents submitted to the court.
IMPORTANT
While a case on the division of property during a divorce is being processed in court, one of the spouses can hide jointly acquired material assets. To prevent this, the judicial authority, at the request of the second party, has the right to take measures to secure the claim in the form of seizure of property, a ban on conducting any transactions with real estate until the court decision on the claim comes into force (Article 140.141 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation) .
Challenging a court decision on the division of disputed property
Court decisions are challenged by filing an appeal. The basis is the court’s failure to comply with procedural norms, violation of the rights of one of the parties: reduction of shares in property, reduction in the amount of compensation, etc.
The appeal is carried out in a higher court of appeal (city, regional, regional).
Deadlines for appeal
The appeal period is 1 month from the date of the decision. After the specified period it comes into force. If a period is missed, the plaintiff or defendant has the right to restore the period by presenting evidence of valid reasons for the omission.
Procedure for challenging a decision
The party who disagrees with the decision has the right to file an appeal, guided by Art. 321 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation:
- The complaint is filed with the court that made the contested decision, then forwarded to a higher authority after the appeal period has expired. The parties to the proceedings receive copies of the documents. The second spouse has the right to object to the appeal.
- A collegial hearing of the case is scheduled at a meeting. The complaint will be considered for no more than 2 months.
- A determination is made to satisfy or refuse to satisfy the complaint in whole or in part.
The appellate court has the right to overturn the decision and remand the case for retrial, as well as distribute legal costs between the parties.
Court ruling for division of property upon divorce and state duty
For property matters of spouses, the jurisdiction of magistrates' and district courts, when filing a statement of claim, it is required to pay a state fee. According to paragraph 1. Clause 1 of Article 333.19 of the Tax Code, the amount of the fee is calculated as follows, depending on the cost of the claims:
| Property value (RUB) | The amount of the state duty is a fixed amount + percentage of the value of the property (rub.) |
| Up to 20000 | 4%, but not less than 400 |
| 20001-100000 | 800+3% |
| 100001-200000 | 3200+2% |
| 200001-1000000 | 5200+1% |
| Over 1000000 | 13200+0.5%, but not more than 60000 |
Moreover, if the property claim cannot be assessed, then the fee for the applicant is 300 rubles (clause 3, clause 1, article 333.19 of the Tax Code). If previously the court made a decision to determine the spouses’ ownership of the common material good, then the state fee for its division, or allocation of a share, is paid in the amount of 300 rubles (subclause 3, clause 1 of Article 333.20 of the Tax Code).
Attention
When submitting an application, which resolves not only the issue of dividing the property of husband and wife, but also requires a divorce, payment of the state fee occurs both for a claim of a property and non-property nature (clause 1.1 of Article 333.20 of the Tax Code).
Jurisdiction for division of property upon divorce at the place of registration of the defendant
The place of registration of the defendant means the locality in which the person registered. When filing a claim for division of property in court, it is advisable for one spouse to have information about where the second participant in the marriage is registered. This factor will speed up the procedure for considering the case, since it will be easier for the government agency to notify the party about court hearings. If the plaintiff has doubts about where the defendant is currently registered, or if the husband or wife’s residential address changes frequently, the court has the opportunity to find out the last known place of registration of the person. But at the same time, you need to be prepared for a possible change in jurisdiction in considering a case on the division of property upon divorce.
What is not subject?
However, not all property acquired during marriage is divided equally between husband and wife. There are a number of exceptions that provide for the transfer of one or another type of property to one of the spouses on the right of personal property, namely:
- Property that belonged to a person before marriage.
- Property transferred to the husband or wife on the basis of a gift agreement, by right of inheritance, or by concluding another gratuitous transaction.
- Personal items for the divorcing couple such as clothing, hygiene products, etc. This category of items does not include jewelry, jewelry and other luxury items.
- Exclusive rights to the fruits of the intellectual activity of one of the spouses.
- Property owned by a joint child or children, including deposits opened in their name.
Jurisdiction for division of property during divorce at the defendant’s place of residence
When filing a claim, the spouse can indicate the place of residence of the second participant in the marriage union, which he knows, and submit documents on the division of property to the court in accordance with this jurisdiction (Article 28 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation). Place of residence is understood as the territory where a person resides permanently or with preferential right (Article 20 of the Civil Code).
IMPORTANT
In cases where the defendant’s place of residence is unknown or is located outside Russian borders, an application for division of property is submitted to the court according to the last known address where the spouse lived (clause 1 of Article 29 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
If the place of residence of the defendant spouse changes, after filing a claim in court, the territorial jurisdiction for dividing property upon divorce does not change.
The court's ruling on the division of property during a divorce at the location of the property
In exceptional cases, claims that consider the issue of division of real estate (building, premises, structure, land plot, etc.) are filed with the judicial authority at the location of this property (Clause 1, Article 30 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
If there are several objects of divisible real estate of the spouses, the plaintiff has the right to choose which judicial body to submit an application to at the location of this property. However, in judicial practice this position is reluctantly accepted. Often this decision comes down to the fact that if there are several real estate objects and they are located in different territories, then the claim should be filed at the location of each of the objects.
IMPORTANT
In addition, the jurisdiction of the case at the location of the real estate is often applied by the courts, if not only a dispute arises about the division of property of the spouses, but also when the right to this property is claimed (Clause 1, Article 30 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
How to remove a seizure from property?
Sometimes, when executing court decisions and sentences, property that is the joint property of a married couple may be seized. A similar measure applies to real estate and movable property:
- automobile;
- Bank deposit;
- securities.
To free the defendant's spouse's share from seizure, the husband (wife) must prepare a civil claim to determine the share in the couple's total property and release it from the seizure. Such actions are carried out at the place where the property is located.
What is contractual and exclusive jurisdiction for the division of property upon divorce?
Contractual jurisdiction implies a change in the competence of the court on a territorial basis by agreement of the participants in the case under consideration (Article 32 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation). The concept is used when dividing property upon divorce, when it is convenient for the parties involved in civil proceedings to better ensure their interests. This agreement is concluded before the court accepts the case into its proceedings. Once a contract is concluded, it cannot be terminated unilaterally.
Contractual jurisdiction is applicable to issues of division of property, but cannot be used to change exclusive jurisdiction (Article 32 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
Exclusive jurisdiction means consideration of cases in courts determined by law. It was created for more convenient consideration and research of case materials, requests for documentation of divisible property, Art. 30 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation.
Exclusive jurisdiction is intended for claims related to any legal aspects in the field of real estate of spouses: ownership, right of use; determination of the order of use; division of real estate that is in shared or joint ownership, and the allocation of a share from it, etc. Art. 30 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
What is the jurisdiction of cases on division of property in case of divorce with children?
When determining jurisdiction for a divorce with children, the plaintiff has the right to file a claim both at the defendant’s place of residence and at his own address if he has minor offspring with him (Article 28, paragraph 4 of Article 29 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation). However, if the consideration of cases is accompanied by the resolution of the property issue of the spouses, it will be necessary to take into account not only patrimonial jurisdiction, but also territorial jurisdiction.
- A divorce in the presence of offspring, even if the dispute about them is resolved by a pre-trial agreement about the children, if there are property claims in excess of 50,000 rubles in the statement of claim, will take place in a district court (Article 24 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
- Claims for the division of property of spouses and divorce can be considered at the place of residence of the defendant, or at the place of residence of the plaintiff, if there are minor children with him, in accordance with paragraph 4 of Article 29 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation. However, the jurisdiction of related cases does not cancel exclusive jurisdiction. In other words, even if there are young children, the case regarding the division of real estate between spouses (for example, rights to a land plot) is considered at the location of the property (Article 30 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
What is the jurisdiction of cases on division of property and alimony during divorce?
Upon divorce, the spouse may raise the issue of division of property and collection of alimony in the application. At the same time, it is worth paying special attention to the jurisdiction of state bodies in resolving these issues. According to Article 23 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, the jurisdiction of the world courts allows the consideration of applications for divorce and division of property of spouses worth up to 50,00 rubles. But at the same time, alimony collections through the magistrate’s court are possible only by filing an application for a court order. Claim proceedings for alimony payments are possible only in a district court. Accordingly, if the plaintiff wants to resolve issues of divorce, provision of offspring and division of property, he should file a claim in the district court.
IMPORTANT
As for territorial jurisdiction, according to clause 4 of Article 29 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, the plaintiff has the right to file a claim for division of property during a divorce not only at the defendant’s residence address, but also at his place of residence.
Proving claims in property disputes
Evidence base:
- the subject of the claim is property. The application shall indicate a complete list with a detailed description. After making a decision on the division of property, the court may refuse to accept a second claim, even if part of the joint property was missing in the first;
- date of entry and dissolution of marriage. Everything acquired during this period will be common property. The application indicates the time of its purchase. Important: if the application states the date when the joint household ceased to exist, then items acquired later are not considered common;
- confirmation that the property was purchased using general funds: account statements, checks;
- the cost of things, their location;
- the plaintiff’s wishes regarding the distribution of common property must be justified;
- the presence of encumbrances on real estate and immovable property: pledge, arrest, etc.;
- if the claim is filed after 3 years after the divorce, then the reasons for the “delay” should be indicated;
- evidence of claims to recognize things as personal property.
Each circumstance must be documented; it is allowed to use the testimony of witnesses. Copies of all documents are attached to the claim. They are sent to the participants in the process.
If there is a large amount of property, an inventory is drawn up with the cost and degree of wear and tear. Then you should not make any enumeration in the application - indicate that a detailed list is attached to it.
If other persons also have rights to property, they are involved in the case. When the disputed property is sold or donated by the other party for its own interests, the property is included in the list, and the plaintiff has the right to monetary compensation.
Problems and nuances
Determining generic and territorial jurisdiction when dividing common property upon divorce may be accompanied by some features and difficulties that should be paid special attention to and taken into account when drawing up and filing a statement of claim.
- When accepting a statement of claim for proceedings, the judge determines the jurisdiction of the case. If it turns out that the issue is not within the competence of this judicial body, the documents are returned to the plaintiff with a determination of where the applicant should apply. However, if the incorrect jurisdiction is revealed already in the judicial process, a representative of the authorities must make a determination on the direction of the case in accordance with the correct jurisdiction. A case sent from another court is accepted by the addressee; Disputes about jurisdiction between courts are unacceptable. (Article 33 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
- If there is a deliberate violation of territorial jurisdiction (for example, the plaintiff concealed the true location of the defendant), and the court has already made a decision, such a verdict can be canceled by a higher authority (Article 330 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
- In situations where the respondent spouse does not agree with the financial value of the divisible property (both common and individual), the husband or wife has the right to petition for an assessment of the value of the property during a divorce. It should be taken into account that after the event, the jurisdiction for consideration of the claim may change.
- The division of common property with a foreign spouse occurs according to the laws of the state in whose territory the disputed property is located (Article 161 of the RF IC).
- Difficulties sometimes arise when determining the jurisdiction of a property claim in a divorce when the defendant is serving a prison sentence. According to the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court No., if the claim is accepted by the court under Article 28 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, then the application is submitted at the last place of residence of the defendant. When dividing real estate, exclusive jurisdiction for the consideration of the case is observed (Article 30 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
Protection of property rights during a divorce requires strict adherence to the principles of tribal and territorial jurisdiction. If the rules are not followed, it is possible to either return the application, transfer it to another government agency, or cancel an already made decision. All these actions will lead to a delay in the consideration of the case.
Comments Showing 0 of 0