Concept of family law
The set of legal norms regulating legal relations between citizens upon marriage, relatives, and persons who have adopted children into a family constitutes family law. Family legislation has certain specifics: the Constitution of the Russian Federation of 1993 refers it to the joint jurisdiction of the Russian Federation and its constituent entities. This regime establishes that a normative legal act can be adopted at the level of the federal government and in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. This is the concept of family law.
At the same time, the law establishes that a legal act must not conflict with the Federal Law.
Consultation with a lawyer on the division of property of the MIP legal group will win a family case with a guarantee of results!
The concept of rule-making in relation to the constituent entities of the Russian Federation is defined in two ways. Subjects can create and issue legal acts in the following cases:
- the legal act issued by the constituent entities of the Russian Federation is assigned by the Code to their jurisdiction;
- the absence in the RF IC of a legal norm that regulates the current legal relationship.
Based on this, the legal act created by the constituent entities of the Russian Federation mainly resolves issues of marriageable age and the organization of the work of guardianship and trusteeship bodies.
What amendments to the Constitution concern family and children?
On July 3, Russian President Vladimir Putin signed a decree “On the official publication of the Constitution of the Russian Federation as amended.” Among the amendments that were approved during the nationwide vote on July 1 were provisions on family relations, family protection and raising children.
The Constitution was supplemented by Article 671, which established that children are the most important priority of Russian state policy. According to paragraph 4 of the new norm, the state creates conditions for the comprehensive development of children in the spiritual, moral, intellectual and physical directions, and also promotes in them patriotism, citizenship and respect for elders. The state also assumes the responsibilities of parents in relation to children who are left without care, but ensures the priority of family education.
In addition, the paragraph “g. 1" part 1 of article 72 of the Constitution. According to it, the Russian Federation and its constituent entities protect the family, motherhood, paternity and childhood, as well as the institution of marriage, which means the union of a man and a woman. In addition, they create conditions for a decent upbringing of children in the family and for adult children to fulfill the responsibility of caring for their parents.
In the new version of the Constitution, paragraph “c” in part 1 of Article 114 was changed. Now it states that the government of the Russian Federation, among other things, provides support, strengthening and protection of the family, as well as the preservation of family values.
How many times can you get married? More details
Principles of family law
The concept of principles of family law is to determine the fundamental principles on the basis of which the branch of law is built. The principles of family law are closely related to constitutional provisions. Principles of family law:
- reveal the concept of what can be considered support from the state for fathers and mothers;
- define the concept of what is a state guarantee of family protection;
- establish the foundations of the constitutional order.
Family legislation is aimed at protecting the rights and freedoms of citizens, and also reveals the concept and tasks of legal regulation. At the same time, the legislator establishes priority universal human values: love, respect, the concept of responsibility of parents to children, mutual assistance of all family members. These principles remain unchanged. It is interesting that the RF IC does not establish the concept of family.
The principles of family law are enshrined in regulations. The concept of each of them is unchanged, and the principles must be followed in marriage and family relations. The principles include the concept that, from a legal point of view, relationships concluded in the form of marriage in the registry office are considered official. Marriage must comply with moral and ethical guidelines, as well as legal norms.
What goals does the legislator pursue when regulating family legal relations?
Family legislation and other acts containing norms of family law pursue the following goals:
- family strengthening;
- inadmissibility of interference in family affairs.
Marriage, as a legal fact, gives rise to legal consequences leading to the emergence of legal relations between the parties specified in the laws.
The family is under state protection and needs guarantees.
Some legal experts consider the position that moral and ethical guidelines are considered the principles of family law as a controversial issue. This is the existence of the institution of family on mutual love, sympathy, mutual assistance. However, it cannot be denied that these principles significantly influence the creation of an atmosphere in the family, and also run as a “red thread” through many provisions of the Family Code.
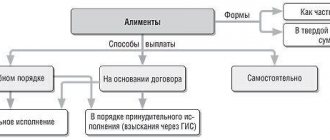
Article 111 of the RF IC. Obligation to report a change of place of work of a person obligated to pay alimony
- The administration of the organization that withheld alimony on the basis of a court decision or a notarized agreement on the payment of alimony is obliged, within three days, to inform the bailiff at the place of execution of the decision to collect alimony and the person receiving alimony about the dismissal of the person obligated to pay alimony, as well as about the new his place of work or residence, if known to her.
- A person obliged to pay alimony must, within the period established by paragraph 1 of this article, inform the bailiff and the person receiving alimony about a change of place of work or residence, and when paying alimony to minor children, about the presence of additional earnings or other income.
- In case of failure to report the information specified in paragraphs 1 and 2 of this article for an unjustifiable reason, the officials and other citizens guilty of this will be held accountable in the manner prescribed by law.
Composition of family law
The sources of family law act as a form of external expression of legal provisions and enshrine them in documents. The following normative legal acts have been introduced into family legislation:
1. Constitution of the Russian Federation of 1993. In Article 7, paragraph 2, the law defined the principle of assistance to Russian families from the state. In addition to defining the competence of the center and regions, the Constitution contains a number of legal provisions, which are reflected in legal acts. For example, these are articles 19, 38, which establish the equality of both sexes in rights and freedoms, as well as the obligation of parents to raise children, as well as the obligation of children over 18 years of age to support their parents.
2. Family legislation, Family Code (No. 223-FZ) defines:
- basic principles;
- the procedure for concluding and dissolving marital relations;
- powers of parents in relation to children (including adopted children);
- parental responsibility;
- application of norms to legal relations in which foreign citizens or stateless persons are participants;
- procedure for judicial protection.
Family legislation is distinguished from previous laws by new provisions introduced simultaneously with the law: on alimony, the procedure for concluding a marriage contract, and the interests of children in foster families.
Family legislation and other acts containing family law norms:
- 143-FZ “On acts of civil status”
- No. 124-FZ “On the basic guarantees of the rights of the child in the Russian Federation”
- Civil Code of the Russian Federation of 1994;
- 44-FZ “On the state data bank on children left without parental care”
Among the sources of family legislation, the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (No. 51-FZ) should be highlighted. In the Family Code you can see a reference norm (Article 4), which points to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation in the event that legal relations cannot be resolved with the help of the RF IC. By-laws at the federal level also cannot be ignored, in particular, the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of 1996 (No. 712), which determines the directions of family policy, in addition, the Resolutions of the highest executive body of power and others. Sources include treaties concluded at the international level. Russia is a party to the Conventions (On the Rights of the Child), the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, etc.
3. International law. The provisions of international treaties take precedence over national regulations. If an international document establishes a different procedure than that determined by national family law, the provisions of international law apply.
Indexation: why, when and how often is it done?
Appointed and calculated in court once in a fixed amount of money, alimony periodically needs to be reviewed, i.e. subject to indexation. After all, life does not stand still, and economic troubles such as crisis and default have become a reality. Hence the need for it does not raise any doubts. It not only protects funds from depreciation, but also saves those receiving them from repeatedly going to the courts demanding an increase in the amount of alimony payments.
Indexation refers to a technique that allows you to maintain the real value of monetary claims and other income against the backdrop of current inflation.
The Family Code of the Russian Federation and the Federal Law “On Enforcement Proceedings,” with amendments and additions, are the main regulatory documents that control processes that directly relate to the indexation of alimony. Their individual provisions reveal the order of its implementation, its size, who should do it and when.
Initially, when assigning alimony obligations, the minimum wage (minimum wage) was taken as the basis, but since 2012 this indicator has become the subsistence minimum. This means that whenever its value changes, the indexation mechanism is activated (Article 117 of the Family Code, Article 102 of Law No. 229 - Federal Law). Moreover, a deviation upward (increase) causes an adjustment in alimony, but a decrease (and this happens) leaves everything unchanged.
It should be noted that the change in the cost of living occurs once a quarter, and all this work is carried out by the government, at the level of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation - by regional authorities according to the laws created by them and accepted for execution. The main criterion is the consumer basket.
Regulations on family law
The peculiarity of normative acts of ministries and departments is that they must be registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation, and also officially published in the Rossiyskaya Gazeta. The deadline for official publication is 10 days from the date of their registration. This rule regarding departmental regulations was established by the President of the Russian Federation in 1993 (Decree No. 104).
Judicial power and sources of family law. Who sets family law? Article 126 of the country’s Basic Law states that, by virtue of its competence, the RF Armed Forces can give explanations on issues of family practice. The practical application of family law norms with clarifications from the highest judicial body becomes justified and correct.
Judicial practice is not included in the sources of family law. An opinion is given in favor of this: the clarifications of the RF Armed Forces are an interpretation of the norms, but do not establish new provisions; the subject of the interpretation cannot be considered a legislator. Considering the fact that the Supreme Court is engaged in studying, generalizing, and analyzing the judicial practice of lower-level courts, the highest court, on this basis, is developing a universal and unique approach to resolving similar court cases in the future. On this basis, the attitude of specialists to the practice of courts and to the possibility of applying it as a source of law has changed over time. Some theories of law establish that the sources of family law should include the Resolutions of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation. For example, issues of paternity and child support obligations (1996, No. 9), issues of adoption (1997, No. 7), etc.
Judicial practice on indexation of alimony
Alimony payments are awarded to the payer for a long period, during which there are repeated increases in the basic calculated values. Due to the fact that the fixed amount of payments is calculated based on the subsistence level of a particular region, as a result of its increase, the amount of penalties increases proportionally. Judicial practice knows many examples of claims filed in court, when a person responsible for a child and concerned about his fate files a claim to force an increase in the fixed amount established by agreement. All sample claims are satisfied, since this provision on increasing the amount of payments is enshrined in the articles of the Family Code.
What legal relations does family law regulate?
The RF IC is designed to regulate personal and property relations between family members. If the relationship is not subject to legal regulation in the RF IC, the norms from the RF Civil Code, as well as other acts, can be fully applied to them. The application of civil legislation occurs under the condition that it does not conflict with the laws. If the legal relations between family members are not subject to the rules of civil law designed to directly regulate the issues that have arisen, the rules governing similar issues are applied to them. This is called analogy of law. If these norms are absent, then the competence of each family member is determined by the main principles of the branch of family law, not excluding the requirement of humanity. This is called the analogy of law. Family law also applies to family relationships involving foreign citizens, as well as stateless persons.
Indexation mechanism
The recalculation is carried out in accordance with Part 1 of Art. 117 RF IC. Indexation by agreement of the parties is no different from that adopted by law, if there is no corresponding provision in the agreement. And if it exists, it should not be worse than what is provided by law. Separate indexation is not provided if payments are made as a percentage of income because this happens automatically.
The law does not establish the exact date when the first recalculation, the second, and so on are made. It is almost impossible to predict when indexing will take place next time. Therefore, the company must constantly monitor compliance with this Resolution.
It is interesting that previously indexation was carried out not based on the subsistence level, as it is today, but was calculated based on the minimum wage. However, from January 1, 2012, the legislator changed the norm. Since then, the basis has been the living wage. Therefore, even if the court decision was made before 2012, and it refers to the minimum wage, then after this time the recalculation is based on the subsistence level.
Other acts of family law
- Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of June 1, 2012 N 761 “On the National Strategy of Action in the Interests of Children for 2012 - 2020.”
- Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of May 14, 1996 N 712 “On the Main Directions of State Family Policy.”
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 18, 2011 N 686 “On approval of the rules for issuing a document confirming the implementation of basic work on the construction (reconstruction) of an individual housing construction project, carried out with the involvement of maternal (family) capital.
- Federal Law of April 24, 2008 N 48-FZ “On guardianship and trusteeship”.
Article 108 of the RF IC. Collection of alimony until the dispute is resolved by the court
- In a case on the collection of alimony, the court has the right to make a ruling on the collection of alimony before the court decision on the collection of alimony enters into legal force; when collecting alimony for minor children - before the court makes a decision on collecting alimony.
- The amount of alimony collected is determined by the court based on the financial and marital status of the parties. The amount of alimony collected for minor children is determined in accordance with Article 81 of this Code.