Question: My husband pays alimony to his ex-wife in the amount of 25% of his earnings. The official salary is 11,000 rubles. The ex-wife files a claim with the court to establish payments in a fixed amount of 10,000 rubles. The judge calls me to the meeting to present his claims, if any. Should I file for child support to reduce the amount of payments for one child?
If you have any questions, you can chat for free with a lawyer at the bottom of the screen or call by phone for any region.
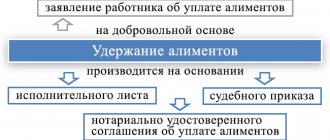
Based on a counter-application for alimony, the court may cancel its decision to collect alimony from the spouse in hard cash. You can draw up an agreement with a notary, which has the same legal force as a court ruling (Chapter 16 of the RF IC). By presenting this document in court, the spouse can avoid the obligation to pay a fixed amount.
Are there any payments?
At the moment, Russian legislation provides for financial support for children only up to the age of 18.
This is due to the fact that this particular limit is the age of majority. In this age:
- a citizen is recognized as a capable, independent, full member of society;
- has the right to get a full-time job;
- gains financial independence;
- becomes the responsible person in the event of the financial insolvency of their parents (it is from this age that they have the right to begin legal proceedings with their child demanding payments for themselves).
Only in exceptional cases is alimony extended or assigned after adulthood.
What innovations were adopted
In 2020, only 1 new law related to alimony payments was adopted. It affects the interests of children raised in state institutions.
Parents pay money for a child from an orphanage, which is spent on his maintenance. Now up to 50% of financial assistance will be transferred to the student’s personal account. Liability for refusal of alimony obligations has also been tightened.
The bills discussed in recent years have not been adopted. These include amendments to the Family Code regarding:
- extending the period of financial support until the age of 23, if a teenager receives higher or secondary specialized education on a full-time, full-time basis;
- extension of alimony payments for adult teenagers who did not have time to graduate from a general secondary institution (school).
The bills proposed for consideration were the parties “A Just Russia” and “United Russia”. The continuation of alimony payments to adult teenagers was provided for in a fixed amount, including expenses for food, office supplies, clothing and shoes.
Do I need to pay child support while on sick leave? The answer is presented in the article “How alimony is withheld from sick leave.” You can find out how to collect alimony from an individual entrepreneur (IP) here.
Special bank account
Despite the fact that according to the law, paragraph 12, part 1, art. 101 No. 229-FZ “On Enforcement Proceedings”, penalties cannot be applied to child benefits, maternity capital or one-time financial assistance; cases of seizure of targeted funds are not uncommon. The problem is that the bailiffs are not obliged to find out the purpose of the money in the debtor’s accounts, and payers need a lot of effort and time to stop the write-off.
To prevent illegal seizure of social benefits, legislators decided to create a special social bank account . It will receive money that cannot be recovered as part of enforcement proceedings. A new bill No. 2211778-7 from July 19, 2020 is being prepared for consideration in the State Duma and can be adopted in 2020.
In what cases are duties extended?
And yet there are cases in which alimony is paid after adulthood. They are mainly related to the child’s health status.
Alimony payments after 18 years of age are possible if the teenager:
- disabled;
- incompetent;
- has a disability group;
- needs financial support;
- not employed.
All issues related to this type of financial assistance are resolved only in court.
Studies
First of all, studying at a university or other form of educational institution is currently not a basis for extending alimony payments.
This is only possible if:
- the alimony payer has a debt (monies will be paid until it is fully repaid);
- the teenager is disabled group I or II.
Upon reaching the age of 18, a child is able to provide for himself independently, even while studying full-time. In addition, budget places require stipends. We are not talking about a commercial establishment at all, even if the case concerns a disabled child.
Thus, only teenagers with serious health problems can count on an extension of payments for the period of education. The court may recognize their right to receive alimony until the age of 23.
For health
To receive financial support after reaching adulthood, the following conditions must be met:
- the teenager is incompetent;
- not able to work;
- needs help;
- does not have a place of work;
- the citizen has I or II disability group.
Group I disabled children can count on lifetime alimony payments.
This degree of health condition is recognized as permanent and incurable. Accordingly, such citizens will always need support.
Disabled people of group II have the right to assistance only if they are recognized as in need of assistance. That is, if there is no opportunity to find a full-time job or have a stable income. If the medical commission cancels the disability group, the teenager will automatically lose the right to alimony payments.
If the disability group was received after 18 years of age due to injury, the teenager may also qualify for alimony.
A parent caring for a teenager may also need financial assistance:
- if group I disability of the ward person is established, and he is recognized as needy, incapacitated and unemployed;
- there are no financial possibilities to provide it.
Such alimony is formalized in a separate court process.
Indexing in a new way
In November 2020, the content of paragraph 1 of Article 117 of the RF IC of Law No. 321-FZ changed. As a result of innovations, employers and other income payers have an obligation to index (recalculate) payments due to inflation. Now this will be done not only by employees of the FSSP service, but also by other individuals and companies who will receive a copy or original of the writ of execution.
Indexation of alimony by the employer makes it possible to better protect the rights of recipients of financial assistance and relieve the burden on bailiffs. A similar obligation was imposed on organizations and individuals paying wages, pensions and other income to the debtor (Article 1, 9 and Clause 8, Part 1, Article 47 No. 229 of the Federal Law dated 02.10.2007, as amended on 05.12. 2020).
What is child support charged until age 23?
If the court recognizes the right of an adult to financial assistance, then alimony will be deducted from the following types of income:
- wage;
- share income from profits;
- annual, quarterly and other types of bonuses;
- pension;
- rental payments;
- scholarship;
- temporary disability benefits;
- unemployment benefit;
- business taxable income;
- cash for overtime work.
In this case, the deduction amount can reach 70% of total earnings. If the alimony payer does not have official employment, the amount of financial assistance is determined based on the average cost of living in the country. This fact is extremely disadvantageous for persons hiding their income.
Is alimony collected from premium payments? The answer is presented in the article “How alimony is withheld from bonuses.” You can find out what to do if your wife has filed for alimony here.
How much should you expect?
When calculating the amount of child support for an adult, the following factors are taken into account:
- the financial situation of the plaintiff;
- the financial situation of the defendant;
- health status, possibility of further employment of the teenager;
- whether the plaintiff or defendant has material obligations to other citizens or the state.
When extending alimony payments, the amount of money is set not as a percentage, but as a specific figure. Its amount should include expenses for food, treatment and rehabilitation.
If the following circumstances occur, alimony payments may be terminated:
- cancellation of disability group;
- employment of an adult;
- death of the alimony payer;
- making a court decision on the lack of need of a teenager.
In any case, the only legal basis for termination of financial support is a court order.
Additional payment for renting housing
Article 86 of the RF IC provides for the possibility of financial participation of parents in additional expenses for children that may be needed in emergency circumstances - serious illness, injury, etc. The need for extraordinary payments, as well as their size and procedure, are established by a court decision. At the same time, legislators assume that, on the basis of Art. 86 parents could also pay housing support. The initiative is being discussed at the Ministry of Justice. It is possible that a new law will appear in 2020. Payment is planned to be collected when it is established that the child does not have housing to rent or partially pay the mortgage costs. Specific methods of involving responsible persons in providing housing for dependents have not yet been approved.
Registration procedure
Extension of alimony payments after 18 years can be arranged voluntarily or compulsorily.
In a voluntary form, the potential plaintiff and defendant enter into an agreement with each other, in which they independently determine the amount and procedure for paying financial assistance. There is no limitation period for alimony issues.
Submitting an application
If a peaceful method is not possible, resorting to the courts cannot be avoided.
At the same time, both the parent or the person replacing him or her, as well as the teenager himself (if he has legal capacity), can apply for alimony.
The application must indicate:
- Full name of the plaintiff and defendant;
- Full name, date of birth of the child (if the application is submitted on behalf of the legal representative);
- directly the facts justifying the payment of alimony (requirements).
The application is submitted to the magistrate's court at the place of residence of the plaintiff or defendant. There is no limitation period for alimony issues.
Package of documents
To file a claim in court you will need:
- passport;
- marriage certificate or divorce certificate (if the claim is filed by the child’s legal representative);
- TIN;
- certificate 2-NDFL from the place of the parent living with the child;
- a certificate or agreement documenting the fact of training;
- medical certificate confirming the assignment of a disability group;
- a certificate from the MFC about the cohabitation of the plaintiff and the teenager (if the claim is not filed by the adult himself).
The court has the right to request other documents. Copies must be attached to all listed documents.
Settlement agreement on payment of alimony
There is an opinion that alimony payments are made only after the divorce. However, a voluntary agreement can be drawn up between spouses at any time.
The form of the alimony agreement is written; the consent of both parties and a notary’s mark are required. Without this, the document has no legal force and is invalid.
The content of the agreement for the payment of alimony must comply with all legal norms and contain the following information:
- Full name, date of birth, place of registration and work of both parties and the child;
- the subject of the agreement is the requirement to pay alimony for a minor child;
- size, procedure and terms of payments.
- the period of validity of the agreement;
- rights, duties and responsibilities of the parties;
- other conditions;
- date and signatures of the parties.
What penalties exist for a defaulter?
Refusal or delay in the payment of alimony is strictly punishable by law.
Measures taken against alimony defaulters include:
- payment of penalties;
- correctional work;
- compulsory work;
- criminal prosecution;
- imprisonment.
In order for a citizen to be recognized as evading payment of alimony, the recipient of the payments must file a claim with the judicial authority. The punishment is determined by the severity of the violation and the amount taken into account against the debt.
The bills that are under consideration include the following measures:
- refusal to issue loans;
- deprivation of the right to drive a vehicle;
- denial of some government services (registration of a foreign passport, visa, etc.).
Also, for non-payers of alimony, travel abroad is prohibited if there is an order from the bailiffs regarding the existence of a debt obligation.