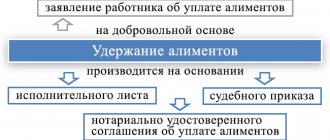
○ Alimony in case of bankruptcy, order of payments.
Alimony refers to the list of types of debt for which the debtor retains obligations even after bankruptcy is declared. Payments are made through debt restructuring or sale of property.
In accordance with the Bankruptcy Law, there is a priority order for payments for accumulated debts. In accordance with Art. 213.27, current debts, which include legal costs, are paid off first.
Claims of creditors for current payments are satisfied in the following order: first of all, claims for current payments related to the payment of alimony, legal costs in a bankruptcy case of a citizen, payment of remuneration to the financial manager, collection of arrears in the payment of remuneration to persons engaged by the financial manager to ensure the assigned he has responsibilities in a citizen’s bankruptcy case. clause 2 art. 213.27 of the Bankruptcy Law).
In accordance with this law, alimony requirements are satisfied first.
Helping your parents is the responsibility of every grown-up child, as gratitude for the upbringing and life they received. This statement is based not only on the morality and foundations of society, but is also enshrined at the highest legislative level - in the Constitution of the Russian Federation.
Is it possible to help your parents financially while in bankruptcy? Let's figure it out together.
According to tradition, first a quote from the law. In this case, the main one, that is, the Constitution.
Able-bodied children over 18 years of age must take care of disabled parents.
Article 38 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation.
With the introduction of the bankruptcy procedure (sale of property), this obligation does not disappear anywhere, but will it be possible to fulfill it, since the debtor will have to live on the subsistence level throughout the entire procedure?
The Family Code says this:
Able-bodied adult children are obliged to support and care for their disabled parents in need of help.
Article 37 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation.
That is, for the obligation to financially help parents to arise, three conditions must be combined:
- Parents are included in the disabled category of the population (pensioners/disabled people of groups I, II or III);
- Parents need help;
- The debtor has an appropriate monthly income.
The financial situation of the parents is not sufficient to satisfy their life needs, taking into account age, health status and other circumstances (purchase of necessary food, clothing, medicines, payment for housing and utilities, etc.).
Clause 9 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2017 N 56 “On the application of legislation by courts when considering cases related to the collection of alimony.”
That is, if the above conditions are not met, then the debtor will have to help his parents within the limits of his subsistence level. If they are met, then during the procedure it is possible to allocate funds for the maintenance of the parents.
There are two options for this. Let's look at each of them.
1. Exclusion of funds from the bankruptcy estate as a dependent of the debtor
If before the bankruptcy procedure the debtor provided financial assistance to his parents, the amount of which was not determined (there is no agreement on the payment of alimony/court decision on the collection of alimony), then the procedure involves the exclusion of funds from the bankruptcy estate as dependents of the debtor.
When considering this issue, it is necessary to prove that the debtor’s parent is financially dependent on him (is his dependent), the following is taken into account:
- Debtor's income;
- Income of the parent (may have his own income, the determining factor is the comparison of the size of his own means of subsistence and the means of subsistence received by the debtor);
- Incapacity for work of a parent (confirmed by a certificate of disability, a certificate from the pension authority);
- The nature of receiving financial assistance (episodic, irregular assistance cannot confirm the presence of financial dependence);
- Availability of other able-bodied children and their income levels.
How do the courts evaluate these circumstances? Here are two quotes from judicial acts.
As for the defendant’s son, he was not working at the time the agreement was concluded; there is no evidence to the contrary in the case materials. From 02/01/2018 to the present, the defendant has been working as deputy director of Spetstekh LLC, and also has two dependent minor children. Having analyzed the income certificate, the court came to the conclusion that his income was only sufficient to provide for the livelihood of himself and his minor children according to the minimum standard.
Taking into account the foregoing, only the debtor will be an able-bodied adult child obligated to provide assistance to his parent, based on his financial situation .
Resolution of the Eighteenth Arbitration Court of Appeal dated April 15, 2019 No. 18AP-3435/2019 in case No. A47-10561/2017.
And the second judicial act
Resolution of the Board of Administration of the Kemerovo Region dated October 26, 2020 No. 569 established the cost of living per capita and for the main socio-demographic groups of the population of the Kemerovo region for the third quarter of 2020 per capita - 9561 rubles, for the working population - 10132 rubles, pensioners - 7681 rubles, children - 9995 rubles. Thus, the debtor needs funds for living in an amount not less than the subsistence minimum, as well as funds for the maintenance of a minor child, for the maintenance of a disabled mother .
Determination of the Arbitration Court of the Kemerovo Region dated January 29, 2018 in case No. A27-24989/2016
How to exclude?
The financial manager has the right to exclude funds in the amount of the subsistence level for the debtor and his dependents independently out of court. However, this specific issue is resolved by the court in accordance with Article 60 of the Bankruptcy Law. That is, the debtor needs to apply to the court that is considering his bankruptcy with a corresponding application.
Who is applying? An application for exclusion from the bankruptcy estate of additional funds for the maintenance of parents is submitted on behalf of the debtor.
If the debtor’s income is the only source of replenishment of the bankruptcy estate and its size is not so large, then, most likely, it will not be possible to exclude funds for the parents, because the balance of interests of the creditors and the debtor will be upset. What is "not so great"? The question is evaluative, a question of judicial discretion and justification of the need for the debtor to exclude these funds.
2. Payment of funds (alimony) from the bankruptcy estate
If the debtor is appointed as the payer of alimony (by court decision/based on an agreement) and there is no debt, then during the bankruptcy procedure alimony will be paid from the funds of the bankruptcy estate as current payments.
Under an agreement to pay alimony.
An agreement to pay alimony, like any transaction by a debtor, is subject to analysis to determine the grounds for challenge.
If the amount of alimony and the procedure for its payment are clearly inflated, excessive and unfair (the amount of alimony is many times higher than the amount of alimony that could be received when collecting alimony in court), then the agreement will be contested.
In this case, one should proceed from the absolute amount of funds allocated to the recipient of alimony and the level of income of the alimony payer. If the amount of alimony exceeds the reasonable sufficient needs of the recipient of alimony for material support, the agreement will be invalidated to the extent of such excess, but in any case, the agreement will remain in force to the extent that would have been collected when establishing alimony in court .
Ruling of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated August 2, 2018 N 305-ES18-1570.
And one more quote from the judicial act.
From the case materials it follows that the agreement on the payment of alimony was concluded by the debtor with the parents almost two weeks before B.I. Simonova’s appeal. to the court with an application to declare oneself bankrupt. Parents of Simonova B.I. are affiliated persons in relation to the debtor and therefore could not have been unaware of the presence of signs of insolvency.
Evidence that the parents of Simonova B.I. are incapacitated, the case materials do not contain it, and based on the 2-NDFL certificates provided by the authorized body, the income of the debtor’s parents exceeds the subsistence level.
The debtor also did not present any reasonable reasons for the need to conclude an agreement on alimony.
Resolution of the Second Arbitration Court of Appeal dated November 23, 2018 in case No. A29-3651/2017.
An agreement on the payment of alimony can also be concluded in bankruptcy proceedings, but only with the participation of a financial manager, in writing with mandatory notary certification.
By the tribunal's decision.
In the absence of an agreement on the payment of alimony, alimony for disabled parents in need of help can be recovered from able-bodied adult children in court.
If alimony is collected from the debtor before the bankruptcy procedure, the writ of execution is transferred to the financial manager, who will then make monthly payments on it.
If the parent decides to collect alimony during the bankruptcy procedure, then he needs to apply to a court of general jurisdiction with a statement of claim against the debtor (his child), and indicate his financial manager as a third party.
What about debt restructuring?
In the debt restructuring procedure, there is no cost of living; the debtor has the right to independently manage funds up to 50 thousand rubles per month. Within this amount, the debtor independently decides how much money will be allocated to support the parents.
○ How to collect a debt?
If the debtor refuses to voluntarily pay the debt, it can be collected by force.
✔ Appeal to bailiffs.
If you have a court order that has entered into force, you can contact the bailiffs who will handle the collection. This method will help if the debtor has property that can be sold.
✔ Going to court.
Alimony debt has no statute of limitations, so you can go to court to receive payments even after an individual loses his bankrupt status (this will happen after 5 years). To do this you need to prepare:
- Application for compensation.
- Personal passport.
- Birth certificate of the child(ren).
- Divorce certificate.
- Certificate of family composition.
- A court decision declaring a debtor bankrupt.
- Confirmation of no payments.
- Calculation of the resulting debt from the bailiffs.
- Receipt for payment of state duty.
Alimony agreement in bankruptcy practice
The inviolability of alimony has given unscrupulous debtors the idea of using the alimony agreement as a means of siphoning off the debtor’s assets.
The scheme is simple.
The spouses enter into an agreement, establish a “decent” amount of alimony, and have the agreement certified by a notary. They present the document in court and demand that the amounts be excluded from the bankruptcy estate.
The courts, at the instigation of other creditors, recognized the trick and applied the rules of law that protect against dishonest behavior of the bankrupt.
Judges carefully study the terms of the alimony agreement and compare them with objective reality.
Important! The terms of the alimony agreement must be related to the financial capabilities of the debtor.
The first thing people pay attention to is the date on which the parents entered into a child support agreement. If the event occurred shortly before the citizen declared himself bankrupt or after the court accepted the application, then this may indicate an attempt to withdraw money from the bankruptcy estate.
The terms of the agreement must correspond to the financial capabilities of the bankrupt. It’s hard to believe that a man with an income of sixty thousand rubles accepted the obligation to pay half a million monthly for his children. Such a condition clearly contradicts the principles of reasonableness and good faith that citizens must follow when exercising their rights and obligations.
In this situation, the interests of other creditors outweigh the rights of the children; the courts come to the defense of the former and declare the alimony agreement invalid.
Under the terms of the agreement, which comply with the usual requirements of the RF IC, the courts do not find any signs of abuse of rights, leave them in force, and the funds paid for children are protected from creditors. Alimony ordered by a court decision is not disputed.
○ Sequence of payments.
After a person is declared bankrupt, the payment of his debts is carried out in strict accordance with the priority order.
✔ Child support debts.
This type of debt is a priority because the legislator, first of all, protects the interests of a minor child. Payment of compensation for alimony debts is made immediately after the entry into force of the court order, if the debt has been restructured. If property is sold, debt repayment is made immediately after the auction.
✔ Debts from creditors.
Claims of creditors for current payments related to one queue are satisfied in calendar order. (Clause 2 of Article 213.27 No. 127-FZ).
Requirements entered into the register are satisfied in the following order:
- For causing harm to life and health.
- For debts on wages and severance pay.
- For other payments.
If there are obligations secured by a pledge of property, 80% of the proceeds upon sale are directed toward these debts.
○ Sale of property to pay off debt.
The procedure for the sale of the debtor's property is regulated by Art. 139 No. 127-FZ.
In accordance with this law, within 10 days from the moment bankruptcy information is entered into the register, a request for a property valuation is made. It takes up to 2 months to determine the cost, after which a corresponding report is drawn up.
Within a month after receiving the report, the bankruptcy trustee submits proposals for the sale of property to the meeting of creditors. After this, auctions are scheduled and the debtor's property is sold. The received amount is used to satisfy the claims of creditors in accordance with the priority.