Home / Parents' rights / Petition to order a genetic examination to establish paternity
In almost all legal proceedings related to confirmation or refutation of a family relationship, there is a need to conduct a genetic examination. Although the court accepts other documentary and material evidence (photographs, letters, medical certificates, witness statements), it is genetic examination that allows one to establish with 100% certainty the origin of the child from the mother or father.
Why?
To determine biological connections, DNA testing is often prescribed. The reasons can be completely different:
- challenging the fact of paternity;
- receiving an inheritance;
- collection of alimony from the biological father, etc.
If a man doubts his relationship with a child, he can undergo a special examination in a certified laboratory and be characterized.
Laboratory test results cannot be recognized as recognition of paternity. Only the court can make such a decision.
How and where is it served?
The prepared text with attachments in the form of copies and originals of documents is transferred in a package to the court office or the secretary of the court session. Documentation must be registered upon submission. Transfer to the office can be carried out at any working time; a request can also be submitted to the secretary of the court session directly in the courtroom.
ATTENTION: If the accused, who is in a pre-trial detention center, submits a petition by mail, then the option of a registered letter with a notification of receipt and a list of enclosures must be selected.
In addition, the request for genetic analysis can be expressed orally, in the presence of the court, with the request recorded in the protocol.
The most effective, but expensive way to obtain accurate information on a particular fact is to conduct an examination. Read our articles about where and under what circumstances you need to submit a request for an examination: construction-technical, land management, auto technical and traceological examination for road accidents, handwriting, repeated judicial and forensic psychiatric.
Who can initiate a DNA paternity test?
The administrative authority has the right to order the procedure. The initiators of its implementation may be:
- participants in court proceedings who are adult citizens of the Russian Federation;
- parents of a child whose relationship is disputed or confirmed;
- guardians;
- close relatives;
- court.
In order to obtain the most accurate information that will allow you to understand the case concerning children, it is better to give preference to this method of confirmation.
Failure Cases
After considering the petition and taking into account the reasons specified in it, the court decides to order an examination or reject it. This right is exclusively within the jurisdiction of the court and cannot be challenged except in cases of violation of court records. As a rule, the refusal is motivated by objective reasons and the obviousness of the situation reflected in the case on the basis of existing evidence.
If the reason for the refusal was technical errors and shortcomings, they are indicated in an extract from the court decision on making a negative decision on the request. They can be corrected and the request can be resumed. In other cases, you will have to be guided by the court decision.
Posthumous establishment of paternity
Determination of paternity is a genetic examination that makes it possible to find out about the fact of paternity or to refute it.
The procedure is prescribed when the father has already died, but was unable to officially register the child in his name. Posthumous recognition makes it possible to:
- a close relative receives part of the inheritance due by law;
- often conducting analysis for obtaining post-death benefits for the loss of a breadwinner, because the test is one of the more accurate options for confirming the fact of relationship.
The applicant may be the mother or guardian. A petition is submitted to the court at the place of registration. Along with it, witnesses who can confirm the authenticity of the information contained in the application are also indicated.
The form indicates that the deceased man is the biological father of the child, and the mother was not officially married to him. It is better to attach facts to the case that can confirm that the father recognized his child.
In some cases, during the proceedings, the court may order a genetic examination. The material is taken from a clinic or morgue, where samples of a deceased citizen may have remained.
Practice indicates that such decisions are extremely rare, but sometimes they are simply necessary to reach a verdict.
Preparing an application
Most often, molecular genetic analysis is carried out to make decisions in civil litigation. During such court hearings, issues of kinship with a particular person may be raised. Any of the participants in the process can apply for a study of genetic material, and at any stage. Most often, claims of this kind are filed by the mother or father of the child, but another man who believes that he is the child’s biological father can also resort to this legal norm.
Paternity can be established not only during the life of a hypothetical father, but even after his death. Gene material can be taken from his bone remains, but this would require exhuming the body. It is much easier to resort to comparing the DNA molecules of close relatives of the deceased, for example, mother, brother, sister, father, and his children from other marriages.
When preparing a petition to establish paternity, you should pay attention to the following points:
- Clearly pose a question, the answer to which must be found by experts. There may be several of them at once, but it is important that they consistently and accurately state what is required.
- When drawing up a document, you must focus on the legislative norms set out in Article 79 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation.
If you have special preferences regarding the choice of laboratory, these can also be stated in the application. The court has the right to reject the proposal and replace the laboratory, but only if there are sufficient reasons for this.
Form
A request for a DNA examination to establish paternity is drawn up in a conditionally free form. This means that no special unified forms have been developed for this. Courts may have developed their own templates for future plaintiffs and defendants or simply have samples of identical documents.
Additional Information
The arbitrariness of the form led to numerous violations that were committed when drawing up the petition. Often, the applicant writes a petition for his own reasons, without focusing on legislative norms, and judicial specialists do not particularly focus on this paper.
A written request to the court to initiate a DNA analysis must be written on an A4 sheet. The petition must have the following structure:
- Preamble – information about the parties involved in the case.
- Name of the form.
- Descriptive part.
- Motivational part.
- Signature of the petitioner and date of filing with the court.
You can enter information by hand or type the text.
Content
There are also many requirements for the content of the application. It is essentially very similar to a statement of claim and must fully disclose the reasons for the current situation and contain requirements regarding the possibility of obtaining indisputable evidence of possible paternity or its absence.
A petition to order an examination to establish paternity is written according to the following template:
- The name of the court where the petition is filed.
- Information about the identity of the applicant, defendant and other participants in the process, if any, - full name, residential address and legal status in the context of this consideration.
- A brief summary of the essence of the current situation.
- Reasons for filing a petition. This may be a desire to establish paternity and collect alimony, or to receive an inheritance left from the father, or, conversely, to challenge the relationship and remove financial obligations from the man. Without specifying reasons, the application will be rejected.
- Legislative grounds for such a study, reference to Article 79 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation.
- Questions to the expert, the answers to which the applicant wishes to receive.
- Details of the laboratory in which the plaintiff wishes to conduct the research.
- The applicant may also demand that a portion of the costs be recovered from the other party or be borne entirely by him in the event of a negative DNA test result.
- List of documents that are attached to the petition.
Important!
If the petition is submitted after the judicial proceedings have begun, within the framework of which the examination is carried out, then a link to it should be given - indicate the number of the case under consideration and the date of commencement of proceedings on it.
The procedure for ordering genetic testing for paternity through the court
During the resolution of the dispute, the judge determines the advisability of DNA testing. Also, any participant in the process can file a petition on the need for this procedure.
If the participants in the trial refuse the analysis, the court cannot conduct it in a forced manner. Even if undergoing an examination is the only way to confirm kinship, the plaintiff may refuse.
The petition must contain the main question that must be answered by the medical laboratory staff. The reasons for the analysis should be stated. The applicant has the right to indicate the laboratory that he trusts to carry out such a procedure.
The name of the citizen who bears all costs related to the analysis should be indicated. If the person declared as the guarantor of payment for the examination evades payment, the amount is distributed evenly among all participants in the trial.
The interpretation of the research results should be carried out by qualified specialists.
Sometimes participants in the process decide to conduct their own analysis in order to present their results in court as strong evidence. Here you need to carefully choose an institution and check the availability of the appropriate license.
If the analysis is ordered by the court, the institution where it needs to be carried out is also indicated. After receiving the conclusion, the judge may invite a specialist to the meeting to announce the results.
About DNA testing
The result of genetic testing can be of two options:
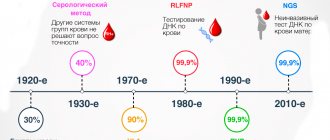
- Probability of paternity = 99.99%, that is, paternity is completely confirmed.
- Probability of paternity = 0%, that is, paternity is completely excluded.
Thus, genetic testing allows us to confirm with 99.99% accuracy that this man is the father of the child. Or completely refute their relationship. Therefore, the court recognizes the results of DNA testing as the most accurate and reliable evidence in the process of establishing paternity.
However, the law does not establish the priority of this evidence over the rest, and the result of a genetic examination is not considered more significant evidence of kinship than others. The court evaluates the conclusion of a genetic examination along with other evidence, but in the presence of controversial situations, it trusts the DNA examination to a greater extent.
That is why applying for a genetic examination is a fairly common practice. Sometimes only this official document forces a man to acknowledge the fact of paternity. But there are cases when this particular document proves that the defendant has nothing to do with the child.
Who is doing the research
When ordering a DNA examination, the court entrusts the examination of biomaterial only to those medical institutions that are accredited to conduct genetic examinations for the court. Therefore, if the plaintiff or defendant presents as evidence a document with the results of an examination from a clinic that does not have special accreditation, the court is unlikely to accept it for consideration.
The laboratory sends the results of the study directly to the court. Transferring the results of genetic testing to any of the parties to the process, except the court, is not practiced.
Purpose and objects of examination
The purpose of genetic testing is to confirm or refute the fact that a child is descended from a specific man.
The objects of examination provided for research may be blood, saliva, or other biological material of the alleged father and child, selected directly at the court hearing by laboratory specialists or other persons entitled to do so. The court may also oblige the parties to appear at a medical institution designated by the court to provide samples for research.
The procedure can be ordered either at the request of one of the parties or at the initiative of the court. Typically, a judge initiates a DNA test in cases where other evidence cannot provide a complete and accurate picture.
Procedure for conducting DNA research
To take a genetic test, you must donate blood to the potential father of the child. In order for the results to be considered correct, it is necessary to undergo the procedure in accordance with all norms of current legislation.
- To initiate the test, you must come to the laboratory and present your passport and child’s birth certificate.
- Blood is donated only in the presence of witnesses who will be able to confirm the procedure in the future.
- After the envelopes containing the tests are misprinted, they are sent to the laboratory for testing.
- The conclusion is sent to the court.
The degree of relationship according to documents must reach a certain level. Undisputed paternity – 99.90%. If the analysis was also taken from the mother, the figure may be slightly lower - 99.75%.
If the conclusion does not answer all the stated questions, the court has the right to order additional research or a repeat test for kinship.
Cases of analysis
Genetic analysis is carried out when it is necessary to establish that the obtained material belongs to the accused when solving criminal offenses. Its principle is that biological tissues found at the scene of a crime, or on the body of a victim, allow identification with the perpetrator who left them at the time of the unlawful act.
For example, on the nails of a resisting victim. The same is important when identifying a criminal using genetic material left behind as a result of sexual violence.
The basis for such an analysis is the receipt of fragments of secretions and particles of skin and hair containing DNA molecules of the accused, which are compared with the material found at the crime scene.
The essence of the examination is based on stable genetic constructs belonging to the individual. By reading the genetic code using new generation technologies, the expert establishes the identity of the polymorphic structure of the samples being compared and establishes the fact of his involvement in the crime.
In civil lawsuits, genetic testing is used to establish paternity or other relatedness. It relies on the identification of so-called variable tandem repeats (VTRs), the basis of human genetic structure. Naturally, the closer the degree of relationship, the higher the coincidence of OTP in genetic samples.