Where to go
To establish paternity, the applicant must apply to the district or city court. The claim is filed at the place of residence of the defendant, with the exception of certain cases when the claim is filed by the mother:
- if the child has a disability group;
- if he is incapacitated.
If there is no opportunity to travel to another city, the plaintiff can send an application to the court by mail. The letter must be registered with a list of enclosed documentation.
The following may file a claim to establish blood relationship:
- mother of the child;
- the child himself after reaching adulthood;
- an authorized representative with a notarized power of attorney;
- government agencies involved in guardianship and trusteeship;
- father of the child.
It is important to note that if the initiator of the procedure for establishing consanguinity with a child is his putative father, then he must personally file the claim and participate in the proceedings. Legal representation is not used in this situation, since the woman may resort to deception to obtain financial gain.
Another important feature of the examination is the consent of the minor if he is over 10 years old. If there is no consent, the procedure will not be carried out.
If the results of the examination confirm the paternity of the participant in the proceedings, the court will make an appropriate decision. The parties will be given a 10-day period to appeal. After its expiration, participants can apply to the registry office with a court order to complete the necessary documentation. The certificate will be issued on the day of application.
How soon can you test your baby's DNA after birth?
You can check your baby's DNA after birth, as soon as the hospital staff has completed all the procedures required for a newborn.
Because an inner cheek swab is used to collect DNA samples, it is important that the baby's mouth is free of meconium, amniotic fluid, or breast milk when collecting DNA.
5 Tips for Collecting DNA from a Newborn Baby or Infant
- Do not feed or give your child water for 60 minutes before the smear test. Failure to follow this recommendation may not change the DNA or affect the test results, but it may contaminate the sample and require the collection of new DNA samples.
- Perform a swab of the child's mouth while he sleeps. It is difficult to perform this procedure with a constantly moving baby, so doing it while he is sleeping is a great solution to the problem.
- Be sure to swab each swab for 30 seconds on the inside of your cheeks, while trying to avoid touching the swab to the gum area
- If the swab appears slightly damp after the swab, simply hold the swab in the air for about 60 seconds before placing it in the paper sample envelope.
- Do not touch the tip of the swab with your hand to prevent introducing foreign DNA into the sample.
Features of the technique
The test will require blood sampling from both parents and offspring. Next, depending on the chosen method, the composition of the collected material is studied.
Humans have 4 blood groups and 2 Rh factors. These blood parameters are set at the genetic level during the conception of the baby and remain unchanged until the end of life. Even procedures such as chemotherapy, blood transfusions, and bone marrow transplants cannot affect the blood type.
A child's blood counts will depend on the combination of his parents' genetic material. The resulting variations will not always be similar to the original sets of genes.
The determinant of the human blood group is the ABO gene, which has 3 forms: A, B, O. Due to the presence of a double set of chromosomes, the following combinations can occur: AA, BB, AO, AB, BO, OO.
How is a paternity test done during pregnancy?
Let's take a closer look at the various ways to conduct genetic testing of the fetus:
- Chorionic villus biopsy . The fetal membrane (chorion) has villi, which, in turn, are part of the placenta. Chorionic villus biopsy is carried out as follows: through the abdomen or vagina of a pregnant woman, the uterus is pierced with a special long needle, through which material is taken for research. A prerequisite for the procedure is its monitoring using an ultrasound machine.
- Study of amniotic fluid . The anterior abdominal wall of the pregnant woman is pierced with a long needle, with the help of which amniotic fluid is removed, which is then transferred for genetic research.
- Umbilical cord blood test . The procedure is complex and risky, since this study requires blood from the umbilical cord blood vessel. In most cases, it is necessary to medically immobilize the fetus, as it can interfere with blood sampling.
- Collection of maternal venous blood . The safest and only non-invasive method of fetal genetic analysis.
To conduct a paternity test, in addition to the genetic material of the fetus, it is necessary to obtain the DNA of the mother and the alleged father. Maternal DNA is necessary to exclude her genetic code from the fetal material.
The following materials can be used for research:
- scraping from the inside of the cheek;
- dried blood;
- nails;
- hair (necessarily with hair follicles);
- sperm;
- earwax;
- any item containing the alleged father’s saliva (chewing gum, cigarette butt, etc.).
Analysis results
The analysis result will be ready within three days to two weeks. There are some difficulties with conducting genetic testing if:
- Potential fathers of the baby are close relatives, for example, brothers or father and son. In this case, testing must be carried out simultaneously with two candidates for paternity, otherwise you can get a positive result in both cases.
- If a woman is pregnant with twins, then analysis is not practiced, especially if several men are applicants for paternity. Since during pregnancy with fraternal fetuses (not twins, when both fetuses develop from the same egg), the fathers of the children can be two different men. In this case, there is no need to talk about the exact result of the DNA test.
Contraindications and risks
The main risks of performing a paternity test during pregnancy are associated with the invasive method. The risk of losing a child exists in the following situations:
- Bleeding begins in the puncture area. If the bleeding does not stop within a few minutes, the life of the fetus is in danger.
- There is a possibility of bradycardia (irregular heartbeat) in the fetus. Usually the situation returns to normal after some time, but in approximately one percent of cases, cardiac arrest occurs in the fetus.
- Threat of infectious inflammation. To eliminate the threat, a pregnant woman must take antibiotics, which can also negatively affect the development of the fetus.
- Threat of retroplacental hematoma (hemorrhage due to detachment of the ovum). Possible when collecting blood from the umbilical cord.
It is advisable to refuse the procedure altogether if:
- Ultrasound examination shows the inaccessibility of tissue for biopsy.
- There are adhesions in the pelvic organs.
- The skin of a pregnant woman, especially in the abdominal area, has infectious lesions.
- The tone of the uterus is decreased or increased.
- There is an exacerbation of any chronic disease.
- Body temperature is increased.
- There is a risk of uterine bleeding.
Cost of paternity test during pregnancy
The cost of genetic testing directly depends on the method of collecting material for research:
- carrying out a non-invasive method (remotely) will cost from 79 thousand rubles;
- research of the genetic material of each additional potential father will cost from 25 thousand rubles;
- a non-invasive method in a clinic will cost from 20 thousand rubles.
Some rules for conducting a paternity test during pregnancy
There are a number of rules that must be followed when conducting genetic testing during pregnancy:
- Challenging or establishing paternity in court before the baby is born is prohibited.
- It is strictly prohibited to force a pregnant woman to undergo the procedure, as it can provoke miscarriage and loss of the child.
- The study must be carried out in a specialized medical clinic.
It is much safer to conduct a paternity test after the baby is born. But sometimes parents cannot wait for this happy event and decide to conduct a genetic examination during pregnancy.
If any conflict situation arises when one of the parents intends to conduct research, qualified legal assistance and support may be needed. You can always seek advice from the specialists of our website. Experienced lawyers specializing in family law will tell you what you will need to do in a given situation, what documents you will need, and what authorities you will need to contact.
You can contact a specialist in two ways: call the numbers provided, or write to a lawyer online.
FREE CONSULTATIONS are available for you! If you want to solve exactly your problem, then
:
- describe your situation to a lawyer in an online chat;
- write a question in the form below;
- call Moscow and Moscow region
- call St. Petersburg and region
Save or share the link on social networks
(
1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
- FREE for a lawyer!
Write your question, our lawyer will prepare an answer for FREE and call you back in 5 minutes.
By submitting data you agree to the Consent to PD processing, PD Processing Policy and User Agreement
Useful information on the topic
Restoration of paternity after deprivation of parental rights
Any mother or father immediately after registering the birth of the baby...
Statement of claim for deprivation of paternity
Deprivation of parental rights is one of the most difficult, especially in...
Statement of claim to challenge paternity
Sometimes men doubt that they are raising their biological children….
How to revoke paternity
Formalize a relationship with the child, if the father wishes to do so...
How to register paternity for a child in a civil marriage
If a baby is born to parents who live in a civil marriage,...
Certificate of paternity
The blood relationship between mother and child does not require additional...
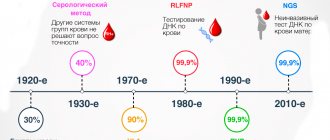
Disadvantages and advantages of the technique
The most important advantage of the method of identifying kinship using blood parameters is its low cost (compared to DNA testing). The price can range from 15 to 75 thousand rubles, which allows the examination to be carried out by a wide range of people.
Another important advantage is the almost 100 percent probability of no blood ties with a minor if the test shows negative results.
The method of identifying kinship based on blood parameters has a number of negative characteristics:
- the analysis cannot be carried out before the baby is born;
- the same blood counts between the father and the minor are not proof of consanguinity, they only indicate its probability;
- insufficient reliability;
- There are cases when an offspring has a blood type that does not match the parent’s. But this fact does not indicate the absence of a blood connection.
What it is?
Previously, geneticists could not establish paternity before the child was born. A little later, methods appeared, but this was associated with an unjustified risk in this case - in order to obtain materials (blood, amniotic fluid, particles of the baby’s epithelium), which can be used to conduct a comparative analysis of the DNA of the potential father and baby, it was necessary to carry out prenatal invasive diagnostics. In other words, we had to puncture the amniotic sac and take materials for analysis. This increases the likelihood of intrauterine infection, miscarriage, and establishing paternity is not a compelling reason for invasive diagnosis.
The current test (NIPT) is not invasive. That is, it is not associated with any risks for the expectant mother and baby, and its accuracy is no less high. Is this research reliable? Undoubtedly. And that's why.
Therefore, the child’s DNA obtained from the research material (about it below) necessarily contains paternal and maternal chromosomes, which make it possible to identify the relationship as accurately as possible.
Basically, you can do tests in two ways:
- apply invasive diagnostics;
- do NIPT (non-invasive test).
In the first case, DNA is isolated from fetal biomaterials: particles of blood, epithelium, water. In the second case, maternal blood from a vein is sufficient - at more than 9 weeks of pregnancy, according to obstetric standards, the baby’s red blood cells partially penetrate into the mother’s blood, which allows them to be isolated and DNA examined.
Variations of inheritance according to blood parameters
Using the table below, you can determine the blood type of the unborn child based on the blood types of the parents.
| Parents | Possible blood type of the offspring in shares | |||
| Blood type | I | II | III | IV |
| I,I | 1 | — | — | — |
| I,II | 0,50 | 0,50 | — | — |
| I,III | 0,50 | — | — | |
| I,IV | — | 0,50 | 0,50 | — |
| II,II | 0,25 | 0,75 | — | — |
| II,III | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 |
| II,IV | — | 0,50 | 0,25 | 0,25 |
| III,III | 0,25 | — | 0,75 | — |
| III,IV | — | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,25 |
| IV,IV | — | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,50 |
As the data show, absolute indicators are determined only if the mother and father have blood type I. But this circumstance cannot guarantee a 100% result, since today you can find a huge number of carriers of this blood type.
Heredity and Rh factor
Determining the Rh factor of an offspring is considered the simplest method for determining blood ties with the putative father. But this analysis also cannot be called reliable, since the offspring may have a negative Rh factor, while the mother and father are carriers of positive Rh. Absolute indicators can only be achieved if each parent is Rh negative. In such a situation, one should expect an offspring with the same blood parameters.
Using the table below, you can determine the Rh factor of the unborn child based on the parents’ indicators.
| Mother, Rh factor | Father, Rh factor | Possibility of a positive Rh factor in the offspring | Possibility of negative Rh factor in the offspring |
| + | + | 0,5 | 0,5 |
| + | — | 0,5 | 0,5 |
| — | + | 0,5 | 0,5 |
| — | — | 0 | 1 |
From the data presented it follows that in almost all cases (except the last one), the possibility of the fetus developing different Rhesus values is equal, therefore the use of this technique is inappropriate for identifying blood relationships between a man and a child.
What does the concept of paternity consist of?
The realities of today are such that an increasing number of couples prefer to do without official registration of marriage, maintaining civil relations.
At the same time, women who give preference to this kind of relationship are at risk of remaining a single mother if the cohabitant refuses to recognize the child as his own. A feature of a civil marriage is the absence of rights and obligations that allow one to present legal demands to the spouse. To be fair, it should be said that the presence of a stamp in a passport also does not always guarantee that the husband will accept obligations to provide financial support and raise the child.
Sometimes this behavior is provoked by the woman herself, for example, when cases of adultery are identified. And sometimes a man simply does not want to burden himself with obligations in relation to a child.
In each of the above cases, the problem is resolved after paternity is officially established. In this case, a biological connection between the child and the man is revealed. After all, paternity is evidenced by the presence of a blood connection between the subjects.
From a legal point of view, paternity is an entry made in a special document that is stored in the registry office, as well as in the baby’s birth certificate. It determines the man who is responsible for the birth of the child, as well as his material support, upbringing and development.
ABO method
This method of studying blood parameters involves focusing on the presence (absence) of antibodies in the blood structure. Each group contains certain antibodies. Below is a table with probable forms according to the ABO classification.
| Mother, blood type | Father, blood type | |||
| I(O) | II(A) | III(B) | IV(AB) | |
| Probability of offspring's blood type | ||||
| I(O) | I(O) | II(B), I(O) | III(B), I(O) | II(A), III(B) |
| II(A) | II(A), I(O) | II(A), I(O) | II(A), III(B), IV(AB) | |
| III(B) | III(B), I(O) | III(B), I(O) | II(A), III(B), IV(AB) | |
| IV(AB) | II(A), III(B) | II(A), III(B), IV(AB) | II(A), III(B), IV(AB) | II(A), III(B), IV(AB) |
The data presented indicate that this technique is more reliable compared to a Rh blood test, but no one can give a 100% guarantee.
Negative results of the analysis
The method of identifying kinship based on blood indicators has one exceptional feature - with its help it is possible with almost 100% probability to refute the blood relationship between the baby and the alleged father.
That is, if, based on the results of the analysis, no relationship was found between the subjects being examined, then the parties do not need to spend money on a DNA test. The judge will make a decision based on the results of the analysis.