Divorce of parents, when children remain with one of the parents, allowed the other not to participate in providing their own children with living conditions. Financial assistance from them often, and not always, ended with the payment of alimony. On February 6, the President of the Russian Federation signed a law that ensures the child’s right to housing after the parents’ divorce.
Important ! Leaving the family is not a reason to get rid of worries and material provision of living conditions for a child left without one of the parents.
Basic provisions
The basic rule governing the division of property between former spouses is contained in Article 34 of the RF IC. According to its provisions, all jointly acquired property, including movable and immovable property, and other material assets, are subject to division between former spouses in equal shares according to the principle of “equality.” At the same time, the law does not distinguish which of the parties actually made a contribution to the family well-being, and what is the ratio of actual financial support to the family budget during the marriage. Spouses have the right to claim equal property rights only to those valuables that were purchased during the marriage relationship, without claiming acquisitions made before and after marriage, as well as to things received by either spouse as a gift or by inheritance. Everyone's personal belongings and gifts are also excluded from the section. The same rule applies to valuables purchased for the needs of common children.
The main principle taken into account during division is that the interests of children should not suffer.
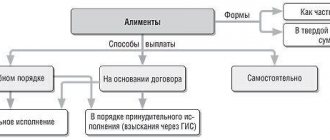
What are additional costs
Sharing additional costs is not new to family law. In Art. 86 of the RF IC has already determined that, in the presence of exceptional circumstances, parents can be involved in additional expenses for the child.
What emergency circumstances are currently provided for:
- a serious illness detected in a child;
- injury to a child;
- the need for additional care for a minor child, etc.
Thus, the list is not closed at this time. However, in practice, most often it is interpreted quite specifically, that additional expenses should be collected if the child’s condition worsens.
Now the list also includes the deterioration of living conditions, that is, the child’s lack of a “suitable for living” facility. The list is also not closed by law.
Cancellation of the 50 ruble child care benefit for children under 3 years old from 2020 - what is important to know?
Rules for property division in the presence of children
When divorcing, the following rules apply to taking into account the rights of a minor:
- Every child is endowed with certain rights from the moment of birth.
- The division of parents' property during a divorce is carried out without the participation of common children as claimants to part of the property.
That is, currently the law does not provide for such a rule as a child’s share in an apartment in the event of a parent’s divorce.
- In the event of a judicial determination of the division order, the rights of minors can be taken into account, which allows one to deviate from the principle of equality of rights of former spouses. That is, the share of one of the spouses when dividing jointly acquired property can be increased by the court, based on the specific needs of the common son/daughter.
- The determination of shares between former spouses cannot be influenced by the presence of property in common children acquired as a gift or inheritance.
- If the process involves real estate acquired with the help of maternity capital, the allocation of shares occurs to all family members in equal shares.
- After a divorce, the child's rights to the father's apartment can only be claimed through inheritance.
USEFUL INFORMATION: How property is divided during a divorce if there are children under 18.
These rules take into account as much as possible the property rights of children who may suffer during the breakdown of the family and division of property.
Who will the child stay with?
Most often, parents independently decide with whom the baby will live. If the spouses could not reach an agreement on this issue, the court determines his place of residence. The following aspects play a decisive role:
- decision of a teenager, if at the time of the proceedings he has reached the age of ten;
- the size of the parents’ living area (each person must have at least 6 square meters);
- income of family members;
- the relationship of the mother and father with the minor, confirmed by witnesses. Usually the teenager's neighbors, caregivers or teachers are interviewed.
The baby lives in the husband’s apartment if it has been confirmed that the mother’s candidacy is not suitable according to any of the above criteria. In practice, children more often remain to live with their mother.
Division of parents' property
Partition in the event of a divorce can be formalized through a voluntary agreement between the former spouses, and if there is no consensus, the court deals with the issue. Minor children do not participate in the division of their parents’ property and, accordingly, do not have rights to their parents’ property allocated during a divorce. At the same time, parents do not have the right to claim real estate and other property registered in the name of a minor.
Despite the general rule of equal shares of parents, there are various circumstances that allow derogations. Clause 2 of Art. 39 of the IC establishes a condition that allows changing the rule for the division of jointly acquired property. In this situation, it is crucial to establish the fact that the common children live with a specific parent. The former spouse, with whom the minor remains after the divorce, has the right to make demands to increase the child’s share in the division during the divorce, as well as to retain possession of his personal belongings and items that he needs.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Can a wife claim her husband’s apartment purchased before marriage?
Do children from a first marriage claim their husband's inheritance?
No person is eternal, and inheritance issues should be taken care of in advance.
Often men pass away in full bloom due to tragic circumstances. And then a serious battle unfolds over the inheritance left by the spouses. In many cases it is almost impossible to reach an agreement peacefully. Offended ex-wives, seeking revenge, do everything to poison the existence of widows.
Children from the ex-wife may well enter into a fight for the square meters left by their dad if they belong to the category of compulsory heirs.
The concept of the term “obligatory heirs” includes:
- minors;
- disabled;
- children who were dependent on their father for a year.
Obligatory heirs can claim their share even if the parent has written a will in advance (for example, for his spouse). Their share will be determined by the court.
Increasing the share of one of the spouses
During the trial, the share of one of the former spouses in an apartment or house may be increased if the following circumstances are established:
- The former spouses have children together who are under 18 years of age.
- After a divorce, children remain in the care of one of the spouses.
- Some exceptional circumstances have been identified that establish the need to take into account the interests of a minor when dividing property.
- The petition to take the child into account when determining the shares is filed simultaneously with the general claim for division.
Of particular interest is the moment of determining exceptional circumstances. This requirement means that it is impossible to apply this rule to all cases of division. During the consideration of the case, the court will proceed from the ability to maintain the level of maintenance of a minor son or daughter properly.
An important point when transferring the consideration of the case to the court is the fact that property rights are taken into account not by allocating a separate share of the child when the parents divorce, but by increasing the share of one of the former spouses with whom the son or daughter remained to live until adulthood. The judge, when establishing exceptional conditions, will make a decision in favor of the parent with whom the young children will remain, ensuring that their needs are fully met. This rule does not apply if common children have reached the age of majority.
How is real estate divided?
The main stumbling block in divorce is the division of joint housing. The court determines into what parts the apartment or house will be divided, taking into account the financial condition of each spouse, and with which parent the children will remain. If the apartment was purchased on credit or with a mortgage, then the payments are divided into two.
How to agree on the division of real estate
If the family has a vehicle, it is also subject to division between the spouses. It doesn’t matter who uses the car, the court offers to sell the vehicle and equally divide the money from the sale.
See also:
Divorce with an adopted child: everything you need to know about it
According to the court decision, only the apartment privatized during their marriage is divided between the former spouses. The process of dividing real estate is complex and is most often accompanied by bailiffs. In many cases, an apartment is divided through a sale, after which the amount received for it is distributed into equal shares.
Features of the section in case of divorce
In addition to real estate, spouses can also divide other items of wealth, furniture, equipment, and vehicles. The exception is items that former spouses use personally. Items and belongings of a minor (clothes, shoes, school things, sports equipment) are excluded from the list considered by the court. Cash deposits registered in the name of a minor are not divided and remain in his possession even after the parents divorce.
The division of property in court will be carried out in accordance with the laws of the Russian Federation. However, in the case of a prenuptial agreement, the terms of the agreement signed by the spouses will be of paramount importance.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Division of property after the death of a husband or wife: how it is done
According to the RF IC (clause 2 of Article 39), equality of shares of husband and wife in property ceases to apply if the following circumstances are established:
- the father or mother did not take any part in improving the well-being of the family, did not have earned income for reasons that the court considers disrespectful;
- embezzlement of property and the family budget by one of the parents was revealed, as a result of which the interests of minors suffered.
In judicial practice, there are often situations when a parent, with whom minor children remain after a divorce, files a petition to increase the share. The court stands up for the protection of the rights of minors, provided that it is proven that the principle of equal shares will lead to a loss of the proper standard of living for the common children.
Rules for participation in additional expenses
Basic provisions of Art. 86 of the RF IC on involving in participation in additional expenses:
- absence of an agreement concluded in accordance with the procedure established by law on the incurrence of expenses;
- the presence of not ordinary, but rather exceptional, extraordinary circumstances that require significant expenses;
- the list establishes that if there is an injury, additional expenses are possible for an adult child, but one who is disabled and in need;
- Both parents can be involved in sharing the costs, and the article says nothing about divorce. Of course, in practice, most often such expenses are assigned to the separately living parent upon separation;
- interrogatory expenses are collected by the court. Also in Art. 86 of the RF IC establishes that all significant issues are decided by the court: they will determine the procedure for participation, the amount, and the presence of exceptional circumstances.
Recommendations for registering property rights for minors
You should be especially careful when registering real estate for young children. In the event of a divorce in such a situation, neither spouse will have rights to residential property, and the judge will exclude this property from the list to be divided (clause 4 of Article 60 of the Family Code). In such a situation, the right to live in the living space will remain only with the spouse with whom the minor remains. And in the future, the father or mother may lose the right of residence if the matured son or daughter does not give his consent to this. Thus, registering a purchase transaction for minors may lead to the loss of all rights to the property of both parents. Moreover, the further sale of such housing is significantly complicated by the need to coordinate the transaction with the guardianship authorities, which will take into account the preservation and improvement of the property status of the children.
How do children influence divorce?
The presence of a child slows down the divorce process of the parents - marriages are dissolved through the court, no earlier than 3 months after filing the documents. If the parties do not agree or there are some disputes, then the process takes longer.
Important! Minor children in the family influence the divorce process.
According to Article 65 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation, the place of residence of children is determined by spouses by mutual consent or by the court. The court is obliged to act in the interests of the minor in order to provide him with the best conditions. Based on this article, it is possible to demand a change in the size of the share of one of the parents.
Personal items
A child under 18 years of age must be provided for by his parents, but he has personal belongings - household items purchased by guardians, clothes, furniture, toys, books that the child uses.
They do not belong to him, but were purchased to provide for him. The division of property does not include the child’s personal belongings - the guardian receives them. Parents are obliged to purchase what is necessary to ensure decent living conditions, health and education for their children. If only the father or mother bought things, during a divorce they remain with the child - the property is not divided like the rest.
Items that were given to a child as a gift or by inheritance are not divided. Until the age of 18, a parent has rights to them; after reaching the age of majority, guardians are required to completely transfer the rights to use.
According to paragraph 5 of Article 38 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation, if an account is opened in a banking institution to which the family regularly transferred sums for children (for example, for future education), this account is not divided.
Personal belongings also include cash benefits: alimony, pensions, personal earnings. None of the parents has the right to appropriate them and use them.
If the baby is under 3 years old, his guardian has the right to demand an increase in the amount, since this period is considered a maternity leave.