Home / Family law / Marriage
Back
Published: 12/30/2019
Reading time: 4 min
3
693
I want to argue with the established opinion that the lack of registration of relationships in a couple is the norm. Society no longer imposes a ban on cohabitation and even defines it as a civil marriage. But from a legal point of view, there is no such thing as a civil marriage if it is not registered. Only those citizens who have registered their relationship by entering this information into the metric records of civil status are considered husband and wife. The remaining couples, in the language of legal concepts, remain in the status of cohabitants.
- Securing the property rights of spouses
- Possibility of inheritance after a spouse
- Visits in prison
- Automatic paternity determination
- Tax benefits for spouses
- Benefits and social guarantees
- Survivor's pensions
I propose to look at cohabitation not from the point of view of morality or the legal status of the couple, but from the point of view of benefits and advantages. In my opinion, based on many years of practice in analyzing litigation, painting a couple is not only a step towards a meaningful relationship, but also a significant gain. I have identified 7 reasons confirming the priority of marriage over unregistered relationships.
Main
A de facto marriage is an unofficial union of two people living together, having a common life and leading a common household. In other words, it is simply cohabitation, which is regulated only by civil law. An actual marriage is a union that is not registered in the manner prescribed by law, so it does not give rise to family relations. People living together in this case are completely free and independent of each other. It is for this reason that many citizens who do not want to bind themselves to the bonds of official marriage choose it.
Introductory information about actual marriage
Thus, this type of cohabitation is informal, unregistered. The relationship does not have legal force, which can complicate processes such as, for example, the division of jointly acquired property or the adoption of a child.
Cohabitants have no statutory obligations to each other. If the Family Code regulates official marriage, the Civil Code regulates residence without a stamp in the passport. And this fact also makes certain adjustments, since relations between relatives and people who are not related to each other are regulated differently.
Previously, a man and woman living together and leading a joint life automatically created a marriage and legislative confirmation of this was not required. Now this type of organization of joint life has many supporters and opponents.
Disadvantages of registration at the registry office
It is enough to think carefully about the consequences of such a decision. As has already been emphasized, civil marriage gives the husband and wife special rights. This is a completely new stage in a relationship that requires a lot of responsibility. Some people simply find it advantageous not to sign. There are not many disadvantages to a civil marriage. These include:
- Responsibility to relatives, spouses and children. Family relations, as emphasized earlier, are regulated by the Family Code of the Russian Federation.
- It is not so easy to end a relationship in the event of conflicts. Actual marriage allows people to simply move away and not think about each other. Officially registered relationships require additional paperwork during divorce.
- Having common children greatly complicates the divorce process.
- After the dissolution of an official marriage, the spouses still have some obligations to each other and to their children. Proving them is not difficult.
That is why everyone decides for themselves what to do. Registration of marriage is a fairly simple procedure. And its termination often means problems. However, the actual marriage requires special attention. What positive and negative sides does it have?
What is a de facto marriage?
Any family legal relationship has form and content.
- A “real” legal marriage is a properly formalized, actually existing cohabitation relationship. The spouses live together, manage their household and consciously formalized their union in the registry office.
- Actual marriage is content without form. People cohabit, run a joint household, support each other, and often have children together. However, for some reason they do not register their union in the registry office.
- A fictitious marriage is a form without content. People register a marriage at the registry office to achieve goals other than starting a family: obtaining registration/citizenship, early acquisition of full legal capacity, minimizing taxes on real estate transactions, concealing belonging to sexual minorities. We are talking here about a mutually beneficial agreement to maintain the appearance of family relationships.
Actual marriage - what is it? In society, this term usually refers to the informal cohabitation of two sexually mature people of the opposite sex. However, recently there has been a tendency to classify same-sex and polygamous unions as actual marriages.
For example, consider the situation in Chechnya. Here, strict adherence to religious norms is ensured through mechanisms of social pressure. Therefore, nikah (traditional Muslim marriage) with a second wife is perceived as legal despite the absence and even impossibility of its state registration.
The second wife initially accepts her specific status and does not require the actual spouse to divorce the first wife. Her property interests in the event of divorce and death of her spouse are ensured by mechanisms outside the legal framework.
In the post-Soviet space, such characteristics as “informal” and “unregistered” are often used as synonyms for the concept of “actual” in relation to marriage. This is completely justified. But the identification of civil marriage and actual marriage is permissible only with reservations.
Characteristic
Despite the fact that people in a de facto marriage live together, run a joint household and even raise common children, they are still considered free citizens, independent of each other. This is very convenient for a man. At one time he has a family and a wife, but by law he is considered single and can marry another girl.
In our state, a de facto marriage is an ordinary cohabitation of two people, which is not regulated by family law. Only children born in such a union are entitled to maintenance from their father if the latter recognizes paternity.
Nevertheless, in Russia every year there are more and more such marriages. Because many young people do not want to take responsibility and formalize their relationship with their significant other.
The essence and origin of the word “wedding”
A modern wedding bears little resemblance to the rituals of the past, which secured the union of two people into one whole - a family. But the essence remains the same - this is an event that becomes the beginning of the life of a new union, family, helps the bride and groom understand this and notifies others.
A wedding makes the couple’s relationship legitimate, that is, legalized and recognized in the eyes of society. In former times, it meant the entry of a new person - a bride into her husband's clan, but now it means the creation of a family by two people. At the same time, their parents and other relatives become relatives both to the son-in-law/daughter-in-law and to each other.
There are several theories regarding the origin of the word "wedding":
- This is a derivative of the name of the ancient Roman goddess of persuasion, the patroness of festivals and fun - Svada.
- It is formed from the verb “to reduce” in the sense of connecting, uniting into one and symbolized the formation of a family from two separate people who were previously strangers to each other.
- It is based on the word “holy,” which emphasizes the sacredness and significance of the union.
- The word comes from the word “matchmaker” and indicates the important role of a person who acts as an intermediary between the families of the bride and groom, a witness to the agreement between them.
- It consists of several words that were significant for the ancient Slavs - “Sva” (sky), “Bo” (gods) and “De” (deed) and denotes the heavenly (important, beyond the control of man) act of the gods.
How is a civil marriage different from a de facto union?
Many people consider the concepts of “civil marriage” and “de facto union” to be synonymous. The actual marriage is recorded in the registry office and has guarantees and obligations approved by the state.
An unregistered union allows lovers to live together, raise children and lead a common life, but the union is not registered by the state.
People are in no hurry to register a relationship and prefer to live together without obligations. There are a number of advantages and disadvantages that actual marriage entails.
Briefly how it differs from a civil marriage
First approach: de facto marriage ≠ civil marriage
Until 1918, only a religious canonical marriage could be officially entered into. Registration of births, weddings, and deaths was the responsibility of the church.
Accordingly, civilians were called:
- marriages of Old Believers, recorded in special metric books;
- cohabitation of people who, for some reason, could not register a canonical church union.
It is noteworthy that the cohabitation of the latter did not have any legal force.
The de facto spouse was deprived of the opportunity to demand division of property after the termination of unregistered cohabitation and could not claim part of the deceased’s inheritance.
According to the instructions of the Council of People's Commissars decree of 1917, a union registered in government bodies was recognized as the only possible form of legal marriage. The wedding no longer gave rise to legal consequences.
The conduct of a religious ceremony was recognized as a private matter for the newlyweds. Despite this, the decree contained a presumption of validity of religious marriages concluded before the end of 1917. Re-registration of such unions according to the new rules was not required.
The understanding of a civil union as a secular union formalized according to the administrative procedure is traditional for the domestic legal system.
The corresponding definition can be found in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia. With this approach, the use of the adjective “civil” is intended to emphasize:
- non-church, secular character;
- state registration in the registry office.
Second approach: civil marriage = actual cohabitation.
The beginning of widespread use of the adjective “civilian” coincided with large-scale ideological and cultural changes (perestroika) in the USSR in the late 80s. Along with the new words “democracy” and “glasnost”, new phrases appeared in everyday life. It was about civil society, self-awareness, responsibility .
Interesting: the term “civil marriage” was used to denote the self-expression of citizens in the sphere of family relationships, free from government interference.
It was about unregistered cohabitation. It is noteworthy that the new approach to civil marriage is reflected in a number of authoritative sources, for example, in the Big Academic Dictionary.
How are civil and de facto marriage related?
First, we need to look at the definition of both types of cohabitation. Civil marriage in generally accepted legal practice is an officially registered relationship between two cohabitants living together in the same apartment, house, leading a common life and, possibly, having children together. A de facto marriage is an unregistered union of two persons living together and leading a common life.
Main signs of actual marriage
Experts from various fields, from psychologists to lawyers, tried to list them:
- open and continuous cohabitation of partners at the same address for a long time, based on mutual feelings such as love, respect, care;
- acquisition of joint property;
- organization of shared life.
Important! Sometimes, but not always, such a sign is the birth of joint children.
Speaking about the signs of a civil (official) marriage, it is worth adding to the list described above only the official registration of marriage in the registry office. Thus, it is clear that civil and actual types of relations have the same basis, the main component of which is cohabitation. As a result of this similarity, in many countries they have the same meaning before the law.
Pros and cons of actual marriage or cohabitation
The advantages of an officially registered marriage quite often tip the scales towards the solemn registration of the relationship. First, it’s worth understanding what marriage gives to both parties:
- each party is endowed with certain advantages, such as the right not to speak in court against their spouse and the like;
- property relations are regulated by law, and not by personal views;
- when a girl gets married, she automatically provides a certain level of security to her children;
- during civil registration, you can conclude a marriage contract, which will clearly state what part of the property which spouse can receive;
- basic psychological comfort and confidence in the future for both spouses.
The disadvantages of an officially registered marriage are limited to the complications of the separation process and the presence of some obligations to the spouse and children even after a divorce.
Pros of marriage (actual):
- the positive component is the complete absence of responsibility to the spouse: in any situation the couple can simply separate;
- Adhering to the same point of view, each spouse can independently decide to break off the relationship, without fear of responsibility before the law, without fear of having to admit to committing something in front of society;
- all property purchased during cohabitation is divided according to the principle of who bought a particular item.
Be sure to read it! How to donate an apartment in 2020: gift agreement, rules, necessary documents, pros and cons of a gift deed
Disadvantages of unregistered cohabitation:
- the emergence of serious conflicts can still lead to legal proceedings using the services of government officials;
- registration of children born in a de facto marriage is difficult;
- Nevertheless, the lack of responsibility to the spouse as such is the main drawback that can negatively affect a couple’s life together at the very beginning.
Property relations play an important role in any type of marriage. In the event of a breakup, a young family does not divide all property in half. Instead, each side simply takes what is theirs. However, things don’t always work out so perfectly. There are also negative components of the division of property in a de facto family.
Note! In such a situation, the division occurs under the control of the Civil Code, and not the Family Code.
This information assumes that the property is being secured as common property. This means that if the husband purchased the car entirely at his own expense, then the wife has no rights to it. However, if the wife nevertheless made some part of the payment, then her share will be taken into account during the division.
Important! Joint labor in actual cohabitation has no force, as well as joint income. But the personal expenses of each spouse are taken into account.
In connection with these rules, we can give an example of how dangerous such a marriage can sometimes be. The couple lived in an unregistered relationship for many years. They built a house on the plot registered to the husband. The wife did not work, but took care of the house and caring for the children. Before retirement, the couple breaks up and the wife is left with virtually nothing. And this is easy to confirm legally, because without working, the woman did not invest a penny in the construction of the house, and her work in caring for it does not matter at the time of division of property. This is not a joke; circumstances may indeed turn out not in favor of one of the parties.
If we discuss how to avoid such a situation, then one of the solutions would be a different budget. Each spouse makes all payments and calculations for himself. Then perhaps the division of property will not seem so unfair.
Every woman must weigh all the pros and cons of marriage after the fact, carefully understanding each of them. Love and, for example, the compatibility of the zodiac signs of the spouses, no matter how bad it may sound, will not have any meaning during separation and division of joint property.
Special cases
Some processes require separate consideration. It happens that a decision to divorce occurs without the presence of one of the parties. The reasons may be different - the inability to physically come to court or the registry office, the disagreement of one of the persons with an official divorce, or the recognition of a person as incompetent, convicted or missing.
The procedure for considering divorce in absentia takes place with notification of the other spouse about the upcoming process. If he does not inform about the impossibility of his presence, the divorce will take place without him. The same applies to the situation if a person fails to appear at the trial twice. As for a convicted person in prison, an administrative procedure for divorce is also possible, even if there are minor children. Filing a divorce from a foreign citizen is also quite difficult, especially if there is a child in the family. In such difficult life situations, it is better to contact experienced divorce lawyers.
Advantages and disadvantages
It is possible to talk about the advantages and disadvantages of the phenomena under consideration only in the context of real relationships between a man and a woman. When both are self-sufficient, have their own income and do not plan to have children, then having a stamp in the passport is not important.
The benefits of state registration of relationships are felt by the vulnerable party, that is, the spouse who:
- does not work because she is busy with housework and raising a child;
- has no income of his own or his income is significantly less than that of his spouse;
- sick, disabled.
From the position of a financially and socially vulnerable spouse, the advantages of marriage are as follows.
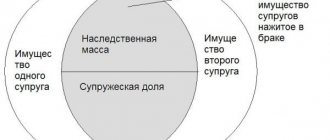
- Extension of the regime of jointly acquired property to assets acquired during marriage through compensated transactions . By default, everything earned by spouses goes into the “common pot” and in the event of a divorce is divided equally. The benefits for those who contribute less to the pot are obvious.
- The wealthier spouse cannot legally sell land, house or other real estate without the knowledge and consent of the marriage partner. The rule is relevant, including in cases where the potential seller is the sole title owner of the asset.
- In the event of a divorce, a spouse disabled for health reasons has the right to claim alimony from the marital partner. And this despite the fact that he is not involved in the deterioration of the health of the future recipient of alimony. Also, alimony can be collected for the maintenance of a non-working pregnant woman or a woman engaged in caring for and raising a child. And this is in addition to child support.
- The surviving spouse is among the primary legal successors along with the offspring and parents of the deceased. Even if the will is not made in his favor, the surviving spouse can claim half of what would be due to him by law (mandatory share).
- A child conceived and born in marriage is recognized by default as the son/daughter of the husband. The husband can challenge the default paternity only in court. Accordingly, in the event of a mother’s divorce, it is easy to collect alimony from the father.
- A marriage certificate confirms close family relationships for all occasions, such as justifying a refusal to testify against a spouse in a criminal case; request for more office space; Resolving a medical emergency regarding an unconscious spouse.
Legal assistance from a lawyer and lawyer
Legal assistance will be needed at different stages of a divorce and even in cases where nothing prevents you from doing this through the registry office. An experienced lawyer will immediately see the pitfalls and tell you how to get around them
Consultation with a lawyer for divorce
At a legal consultation you can get answers to a variety of questions. Most often, spouses are interested in how to divorce without the consent of the spouses, what laws can be referred to, what documents to collect. Each divorce process has its own characteristics that must be taken into account. Therefore, divorce without legal advice is not a good idea.
Price for a lawyer's services in case of divorce
The cost of legal assistance for divorce depends on many factors. The main thing is the complexity of the process. If you need to prove a fictitious marriage, draw up a statement of claim with several demands, collect evidence in favor of the plaintiff, then the price tag can be increased several times. Much depends on the region. So, a consultation in the regions will cost approximately 300-500 rubles, and in the capital at least 1000 rubles. As for the scam itself, the starting price starts at 15,000 rubles.
| Services of lawyers and advocates | Price |
| Initial free consultation (up to 30 minutes) | FOR FREE |
| Consultation in writing | from 2000 rub |
| Drawing up an application for a court order | from 1000 rub |
| Drawing up the necessary documents: claims, complaints, requests | from 3000 rub |
| Representation in court | from 5000 rub |
| Turnkey legal protection: from claim to victory | from 15,000 rub. |
| Appeal, defense in a higher authority | from 3000 rub |
| Assistance in the execution of a court decision | from 3000 rub |
Divorce if there are children
If both spouses have the same opinion about the place of residence of the children and the procedure for providing for them, then a settlement agreement is drawn up. This is the simplest option, but it cannot be done without the help of a lawyer. If you have to act through the court, then you cannot do without the help of a good lawyer - you need to navigate the legislation in order to choose the most advantageous tactics and protect the interests of the plaintiff and children. Without a legal education, this is difficult to do.
Divorce from a foreigner
Many difficulties arise when one of the spouses is a foreigner and permanently resides abroad. According to Russian laws, the defendant must be notified of the beginning of the divorce, in addition, he has the right to be present when the issue is considered in court.
The assistance of a lawyer is necessary for drawing up a statement of claim, a power of attorney to represent the interests of the defendant in Russia, and collecting the necessary evidence. If you entrust the procedure to an experienced lawyer, there is a greater chance of a favorable result.
Filing an application for divorce
The preparation of all documents, including the preparation of a statement of claim, requires special care and knowledge of the rules of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation. A qualified lawyer will help:
- collect the necessary documents;
- fill out applications at the registry office;
- draw up a statement of claim;
- write a petition for installment payment of the state fee;
- draw up a power of attorney for the representative.
Delegating these issues to an experienced lawyer saves spouses from unnecessary hassle and greatly simplifies the divorce process. You can be sure that the interests of each party will be respected.
What the law says
Due to the difficulties of registering marriage in the post-revolutionary and war period, open cohabitation and joint economic activity between a man and a woman were equated to legal marriage. The adoption of the Code of Laws on Marriage, Family and Guardianship of the RSFSR marked the recognition of legal force for de facto marital relations. This practice is typical for the period 1926 – 1944.
Information: in 1944, two decrees of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR were adopted. The first of them, dated 05/08/44, deprived cohabitation of legal force. Citizens living together were asked to formalize their relationship with the relevant government agencies.
It is noteworthy that during registration, cohabitants were asked to indicate the period of actual cohabitation. That is, the relationship was actually registered “retroactively.”
The second decree of November 10, 1944 gave the de facto spouse of a person who died or went missing during the Great Patriotic War the opportunity to apply to the court for marriage registration.
The court decision could be used to enter into an inheritance and receive benefits due to widows of veterans.
The 1969 Code on Marriage and Family did not deal with marriage-like relationships. The possibility of recognition of cohabitation remained only in relation to persons who lived together before 1944. It is noteworthy that it still exists, about which a corresponding note has been made in the current Civil Procedure Code.
In modern Russia, marriage can only be registered. Unregistered cohabitation is outside the legal framework. There is no intermediate institution between marriage and cohabitation.
Important: civil procedural legislation does not imply the possibility of recognizing cohabitation as a marriage for the purposes of inheritance, collection of alimony, or establishment of paternity.
The answer to the question of whether de facto marriages are currently recognized is clearly negative. It is believed that cohabiting people deliberately did not want to apply the corresponding legal consequences to their relationship. The only exception concerns the admissibility of recognizing as marriage a union of persons formed before 1944.
To describe the phenomenon of extramarital cohabitation in Russian judicial practice (in particular in criminal cases), terms such as “actual marital relations” are used.
Despite the name, legal force is not given to cohabitation. In the scientific literature you can find the category “marriage-like relationships”, which, recently, has begun to be used in relation to homosexual couples.
The regulation of the issue under consideration in modern Russia differs from the position of the legislator in many other countries. In France, there is the institution of civil partnership, which is a simplified form of marriage. Actual marriage partners are subject to certain mutual obligations. However, their circle is narrower than that of official spouses. In Germany there is an institution of marriage-like living communities. This form of relationship is available, among other things, to same-sex couples.
The civil procedural legislation of Ukraine provides for the possibility of recognizing de facto cohabitation as a marriage through the court in special proceedings. The corresponding court verdict can be used to substantiate demands for the division of common assets, the collection of alimony for the maintenance of a former marital partner, and inheritance.
Results
From now on, it is clear how actual marriage relations differ from those formalized in the registry office. We can say that this arrangement means the freedom of the spouses, the absence of responsibility and any guarantees. Therefore, officially formalized relationships are considered to be a more reliable union. In addition, neither the state nor the church recognize cohabitation. Such relationships are often regarded as fornication and a mockery of the institution of family. However, it is not always possible to register with the registry office. This is especially true for people with non-traditional sexual orientation in Russia. Actual marriage is an intermediate link between the statuses of “boyfriend and girlfriend” and “husband and wife.” A normal stage of a relationship that should not be delayed. Everyone decides for themselves how to live. But a civil marriage gives spouses special rights, duties and responsibilities.
Legal force of actual marriage
In modern Russia, cohabitation does not entail consequences. Relationships between partners are built solely on personal trust. What does actual marriage mean? Yes, absolutely nothing.
The material side of the issue. The regime of jointly acquired assets does not apply to the assets of cohabitants, either by default or by contract.
Each of the cohabitants is the owner of things acquired by him personally.
That is, the title owner is considered the sole owner.
Caution : theoretically, jointly purchased property can be recognized as common property. However, proving the fact of a joint purchase is difficult. It is difficult to find out the source of funds for which the relevant assets were acquired, as well as their ownership by cohabitants.
The question of the possibility of collecting alimony in the event of termination of cohabitation is not even considered. Cohabitants can inherit from each other only as dependents (eighth priority by law).
The paternity of children conceived in cohabitation is recognized only with the consent of the biological father or by a court decision. The procedure is the same as if conception occurred from a casual relationship. The status and scope of rights of an illegitimate child are the same as those born in a traditional family.
On the recognition of marriage
If you prepare in advance, then recognizing the actual type of marriage will not be difficult. To do this, you will have to prove running a joint farm. Are de facto marriages currently recognized? Yes, but only through the court. The following can be presented as evidence of a relationship:
- recordings of telephone conversations;
- joint photographs;
- correspondence;
- witness statements;
- video materials;
- medical reports (in case of acknowledgment of paternity);
- payment slips confirming joint purchases.
In fact, anything that can indicate a relationship between two people serves as evidence in court. Recognition of the actual marriage takes place. All of the above evidence helps not to recognize the marriage as officially registered, but to indicate the conduct of a joint life, emphasize the presence of shared ownership and kinship with children.
Question about real estate
The severance of a de facto marital relationship is not a guarantee that a couple will divide property without conflict situations and will not go to court. In this matter, former lovers will be helped not by the Family Code, but by the Civil Code. All things acquired by citizens during cohabitation are considered the common property of the cohabitants.
Be sure to read it! What happens during a divorce if the apartment was purchased during marriage, but is registered in the name of one of the spouses?
If the man did not invest money in the purchase of the apartment, and the woman purchased it at her own expense, then she will have all the rights to the living space. If the couple invested money equally, then the court will consider the case so that each of the cohabitants receives the share that they claim based on the investments.
Property
What to do with common valuables if a man and woman decide to end their informal relationship and break up? This question is asked by many people who find themselves in a similar situation. After all, an unofficial union of two people is an actual marriage. The division of property in this case will be carried out in accordance with the norms of civil law, and not family law. In addition, each spouse will have to prove their right to the thing and the fact of its acquisition. If property purchased during a legal marriage is considered the joint property of the husband and wife, then during the period of cohabitation it belongs only to the person to whom it is registered.
Example
The young people met and after some time decided to live together. They were in no hurry to formalize the relationship. However, during the actual cohabitation, the man purchased a new car with the money of his common-law wife, which he registered in his name. Two years later, the couple separated, and the ex-wife decided that she had every right to return half the cost of the car. The man was against it. She could not prove the fact that the woman gave him money, because she did not have any evidence (receipts, etc.). Accordingly, the car remained with the former common-law husband, since according to the documents he is its owner.
Pros of civil marriage
The official form of joint farming has its advantages and disadvantages. What is it about? First of all, it is necessary to find out why the population is attracted to painting in the registry office. Why register relationships if you can do without this feature? The fact is that among the main advantages of a civil marriage is the security of family relationships. After registration at the registry office, citizens will be considered official spouses. Their relationship will be regulated in accordance with the Family Code of the Russian Federation.
In addition, civil marriage:
- Gives husband/wife special rights. For example, in some hospitals, only official spouses are allowed to visit patients.
- Gives the parties security and clarity of relations of both a property and non-property nature.
- When children are born, official marriage eliminates most problems. For example, children will be able to take their father's surname without additional paperwork. In addition, parenting is easier in a formal relationship.
- The division of property during a divorce will be carried out in accordance with the RF IC. In addition, spouses can enter into a marriage contract in advance. It will help clarify the principles of division of common property.
Accordingly, this form of relationship provides certain guarantees. As already mentioned, de facto marriage still occurs quite often in Russia. Why are citizens in no hurry to formalize relationships?
Children's situation
Babies born in a de facto marriage have the same rights as those born in an official union. But for this it is necessary for the child’s father to acknowledge his paternity and write a statement to the registry office. Otherwise, the baby’s mother will be considered a single mother, since the people’s marriage was not officially registered.
In practice, situations very often occur when women have to prove the paternity of their “common-law” husbands in court in order to receive at least some funds from them to support their children. Such cases are far from isolated. While in an official union, the woman’s husband becomes the child’s father automatically even when the baby is born within 300 days after the divorce.
Due to such problems that may arise in the future, many women do not want to enter into an actual marriage. Children born in an unofficial union are deprived of the opportunity to live in a full-fledged family and receive support from their father, especially if the latter turned out to be not a very decent person and refused to recognize and formalize his paternity.
The condition of babies born in a de facto union
A child born in a de facto marriage has the same rights as a child born in an official marriage. To do this, the baby’s father needs to confirm paternity and submit an application to the registry office.
If this does not happen, then the child's mother will be considered a single mother, due to an unregistered union.
There are many situations when women prove the paternity of a child, while going to court to receive funds to support the baby.
Looking at the problems, girls refuse actual marriages and have children only in an official union. They believe that a child should live in a full-fledged family under the care and support of both parents.
Alimony
To collect alimony, it is not at all necessary to be bound by legal ties. To receive alimony from the biological father, an appropriate entry on the fact of establishing paternity in the child’s birth certificate is sufficient. In this case, it is absolutely not necessary to have a marriage registration certificate. In accordance with the current Family Code, the basis for the emergence of the right to alimony is the birth certificate. The absence of an officially registered relationship between cohabitants is not a reason for refusing to grant alimony , although clarification of all the circumstances in this case significantly delays the legal process. If there is no record of the father on the birth certificate, it will be necessary to prove the fact of an informal relationship or achieve voluntary recognition of paternity. Establishing paternity gives the child the legal opportunity to receive funds from the father for his maintenance.
About legal consequences
Are de facto marriages currently recognized? Quite. In court, if desired, you can prove the fact of running a joint farm. But in practice such cases are extremely rare. What are the legal consequences of unregistered relationships? Among them are the following features:
- children do not receive their father’s surname “by default”;
- the father can assign his surname to minors only after recognition of paternity;
- Anything acquired during marriage is not considered joint property.
Important: children born in a civil and de facto marriage have the same rights. The only difference is that in the second case you will have to prove your relationship with the father. For this purpose, genetic testing was invented long ago.
Inheritance
The lack of official registration of family relations causes certain problems in the event of the death of one of the members of such a family. Regardless of the period of cohabitation and the amount of property acquired during this period, after the funeral a dispute over property will arise with the legal heirs. The absence of a will and living in a de facto marriage are grounds for refusal to receive an inheritance; common-law spouses do not belong to any of the queues provided for by law.
Cohabitants try not to think about situations related to each other's death. In practice, in such situations, it is almost pointless for persons who have not officially registered their marriage to declare property rights . The courts take the side of the law, which does not recognize or regulate the relationship between the parties in a de facto marriage.
There are rare exceptions
In exceptional cases, the court stands up to protect the property interests of the cohabitant in the event of the death of the common-law spouse. Judicial practice contains similar cases. Applicants manage not only to prove their residence in an unregistered marriage, but also to receive part of the property commensurate with the costs of its acquisition. It is enough to provide the court with evidence containing information about the funds contributed (including those exceeding the expenses of the deceased common-law husband or wife) when purchasing property in the ownership of the deceased common-law spouse.
Registration of relations
Marriage, legal and actual, implies a certain behavior of citizens. The fact is that in the first case you will have to officially register the relationship, for example at the registry office. But in actual cohabitation, no such manipulations are necessary. Marriage registration is handled by the Wedding Palace. Citizens who decide to become husband and wife must:
- Collect a certain package of documents. Usually the passports of the parties are sufficient. If the bride is pregnant, in order to speed up the registration procedure, you can bring a doctor's certificate with you.
- To write an application. It is filled out at the registry office.
- Pay the marriage registration fee. Today in Russia such an operation will cost 350 rubles.
- Set a date for painting. Usually on this day people celebrate their wedding.
- Wait until the relationship is registered. On the appointed date and time, come to the Wedding Palace, confirm the operation and receive a certificate in the prescribed form.
In fact, everything is much simpler than it seems. However, not everyone can enter into a civil marriage. What restrictions exist in Russia?
Is such a union valid in Russia?
The concept of “actual marital relations” appeared in the family law in the USSR from 1926 to 1944. In modern Russian legislation, the term “actual marriage” is not used. Only a union registered by the state is recognized as valid.
But the judiciary, if necessary, can operate with such concepts as “actual marital relations” to determine the status of citizens living together. In the comments to the Family Code, the concept of “cohabitation” is also found.
So, Russian laws recognize only one type of marriage - civil, registered in the registry office. Society itself, however, accepts other forms of marriage-like relationships: de facto, informal marriage or cohabitation. A family is created in both cases, but in the first it is considered a legal transaction, and in the second it is not.
The actual state of the relationship is not a legal marriage. Only a registered union will have legal consequences that relate to the following basic life situations:
- Issues of providing for children in the event of termination of marriage, and their further education.
- The question of the future fate of the children (who they stay with after the end of the marriage).
- Property relations in terms of jointly acquired property and its division after divorce.
- Housing issue regarding cohabitation after divorce.
- Issues of property inheritance.
Accordingly, if the marriage is not registered in the manner prescribed by law, no family rights and obligations arise between cohabitants.
However, today there are many cases in judicial practice when de facto marital relations received official recognition. Most often, this status is achieved by spouses when dividing property acquired in such a union.
Legal consequences of actual marriage
Sometimes de facto marital relations are recognized; judicial practice has many precedents in which de facto marriage is considered real. But this does not always happen.
Brief legal consequences of such a union:
- An actual marriage does not provide legal guarantees regarding the payment of alimony. This means that spouses must independently decide who, in what amount and how will pay alimony to their joint children.
- The sphere of personal relationships in this type of residence is regulated by the same rules as in an official marriage.
- In the event of the death of one of the spouses, the second does not acquire the right of inheritance, as happens with the civil registration of a marriage.
- Recognition of children born in a de facto relationship is carried out by parents voluntarily.
The informal way of registering a relationship presupposes the existence of rights similar to the rights of spouses who have officially confirmed their relationship. However, there are some restrictions that relate primarily to property relations. At the same time, in an actual marriage, the process of separation is greatly facilitated. Each couple independently decides how to organize their relationship, but it is still worth studying all the nuances of the various methods.
How to divorce
According to Russian laws, in order to get a divorce, the initiative of one of the spouses is sufficient. Even if the second of them is categorically against it, the divorce will take place, but the procedure itself will ultimately take more time.
Both the wife and the husband can file for divorce. True, in this case there is one exception. If the spouses are expecting the birth of a child or the child is not yet one year old, the husband can initiate a divorce only with the consent of the wife. Otherwise, there is no point in submitting an application to the registry office or a lawsuit - the documents will not be considered. This applies to cases where the child was stillborn or died in the first months of life - you will still have to wait a year.
You can get a divorce through the registry office or by going to court. The choice of option depends on whether the spouses were able to agree on the division of property, determining the place of residence of joint children and other points. If both parties agree to divorce and have no mutual claims, you can contact the registry office. True, there are exceptions here, which we will discuss below.
Divorce does not occur on the day of application to the registry office, but no less than a month later. This point is specified in the current legislation and has no exceptions. A month after submitting the application, you need to come back to the authority for a divorce certificate. The same must be done if the divorce took place in court and the claim was granted.
Legal assistance from a lawyer and lawyer during divorce
Each case is unique and may have certain pitfalls. Spouses do not always have the opportunity to divorce through the registry office, and when going to court, they need to prepare documents, correctly draw up a statement of claim, and prepare an evidence base. Not every person can do this.
Most often, the help of a lawyer is needed in the following cases:
- recognition of marriage as invalid or fictitious;
- the presence of disputes about the child’s place of residence or his financial support;
- disagreement regarding the determination of property rights or the procedure for dividing property.
In such cases, it is unreasonable to rely on one’s own strength without a legal education and the necessary knowledge. It is much more effective to entrust the case to a specialist who will conduct the case in compliance with the law and the interests of the plaintiff. It wouldn’t hurt to consult a lawyer in cases where there are no visible problems. Perhaps they will be revealed upon careful study of the situation.
Reasons and grounds for divorce
Russian legislation does not indicate the exact reasons why a marriage can be dissolved. However, if you look at the first chapter of the Family Code of the Russian Federation, you can find a statement that a family is built on the principles of responsibility, mutual love, mutual respect and mutual assistance. It can be assumed that violation of these conditions can be a compelling reason for divorce.
In practice, the reasons may be the following:
- loss of feelings by one of the spouses;
- drunkenness, gambling, drug addiction;
- beatings, cruel treatment, humiliation;
- low income;
- unwillingness to fulfill the responsibilities of a parent.
Incompatibility in the intimate sphere, as well as the fact of adultery, can be reasons for divorce, however, family lawyers do not recommend indicating them in the statement of claim due to the need to maintain the secrecy of personal life. In exceptional cases, it is possible to request a closed hearing of the claim.
No one will dissolve a marriage just because the spouses wanted it that way. on the basis of Art. 22 of the RF IC, it is clear that the determining factor is the impossibility of further cohabitation and preservation of the family. Therefore, the wording specified in the application must be extremely accurate and convincing. Facts of beatings, alcohol or drug addiction must be documented, and statements about the presence of a spouse with a second family must be confirmed by adult and capable witnesses. If the plaintiff does not have evidence of this kind, it is unreasonable to indicate such reasons.
In situations where spouses have a child under the age of majority, the court may find personal reasons unconvincing for divorce. In this case, the plaintiff indicates domestic or financial reasons. You can refer to Article 89 of the RF IC, which states that spouses are obliged to provide each other with material support.
Divorce with or without mutual consent
Divorce in Russia is possible both with the consent of each spouse and on the initiative of one of them. In the first case, it will be easier to resolve the issue: just visit the registry office at your place of residence and write an application. The marital status will be considered and, if the spouses do not have minor children at the time of filing the application, then within a month the divorce will be registered with the state.
In a situation where the initiative for divorce comes from only one party, you can also act through the registry office. There must be a serious reason for this, which is determined by the RF IC:
- The second spouse is in prison, and his term of imprisonment exceeds 3 years. The fact is confirmed by a copy of the court verdict.
- The second spouse is declared incompetent.
- The second husband is listed as missing.
In all other cases, you will have to file a claim in the magistrates or district court, otherwise you will not be able to get a divorce. At the same time, you need to be prepared for the fact that the divorce will last longer: the judge will thoroughly check the evidence provided, has the right to give additional time for reconciliation, and it will also take many days to collect the necessary documents. You need to go to court if one of the spouses does not agree to a divorce, you have common minor children, or property disputes have arisen.
Documents and application for divorce
The easiest way is to write a divorce application to the registry office; here you will need to collect fewer documents. When divorcing in court, you will need to prepare more thoroughly, competently draw up a statement of claim, and try to collect evidence for your arguments.
If there are grounds for divorce through the registry office, you need to prepare the following documents:
- application for divorce (form No. 9), written by the spouses;
- passports of the spouses or one of them, if only the husband or wife wants to divorce;
- original marriage certificate;
- documentary evidence of the grounds for unilateral divorce;
- receipt of payment of state duty.
If one of the spouses cannot visit the registry office for reasons beyond his control, but is not against the divorce, then an application on form No. 10 is filled out. For situations where a unilateral divorce through the registry office is possible, Form No. 11 is provided. If the marriage is dissolved by a court decision, an application in form No. 12 is filled out to obtain a certificate of this from the registry office. The forms of these documents can be obtained by visiting the registry office at your place of residence, where you can also see a sample of filling out.
You must provide documents in person. If for some reason this is impossible, but both spouses agree to divorce, you can write a statement and have it certified by a notary. The prisoner's application can be certified by the head of the colony.
In addition, it is possible to submit an application through the State Services portal. To do this, each spouse fills out an electronic application in their personal account, and the state fee is paid immediately. As in other cases, the marriage will be considered dissolved one month after submitting the electronic application.
If you have to get a divorce through the court, you will need to collect more documents. Some of them are mandatory in all cases, while others are collected based on the specifics of the case. In order not to miss anything, it is better to consult with a lawyer who will tell you what documents are best to collect in a particular situation.
The minimum required list of documents for divorce through the court:
- A statement of claim drawn up in strict accordance with the norms of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, containing information about the plaintiff, defendant, their details, the essence of the claim, references to legislative acts, and a request for divorce. It may additionally indicate a requirement for alimony payments or division of property.
- Passports of husband and wife (originals). If the defendant is against the divorce, only the plaintiff provides the passport.
- Photocopies of birth certificates for each minor child of the spouses.
- Marriage certificate (original).
- Receipt of payment of the state fee (except in cases of payment in installments or deferred payment, for which an application must be submitted).
In some areas of the country, an extract from the house register or a certificate about the family composition of the plaintiff and defendant may be required. This information can be clarified in the court office at the place of residence of the plaintiff, or the defendant, if the statement of claim will be sent to the court at his place of residence. Most often, documents are submitted at the location of the defendant, but there are exceptions. The defendant must be in another city, and the plaintiff cannot go there for health reasons or due to existing minor children.
Documents are sent to the magistrate's court if both spouses agree to a divorce, but have minor children together, there are no property disputes or its value does not exceed 50,000 rubles. In cases where it is necessary to determine who will pay alimony and in what amount, or there are property disputes regarding objects worth more than 50,000 rubles, as well as in situations where one of the spouses is against divorce, the documents are sent to the district court. This can be done in person by visiting the court office or sending a package of documents by mail.
Divorce through State Services, MFC, Civil Registry Office
As of 2020, you can submit documents for divorce through the Civil Registry Office, MFC, or electronically through the State Services portal. The only exception is for cases where one of the parties does not agree to a divorce, the spouses have common minor children or there are property disputes - then the issue can only be resolved in court.
When contacting the MFC, you need to understand that the institution acts only as an intermediary between you and the registry office; its employee cannot dissolve the marriage. They will only accept your documents and transfer them further; this is where the functions of the MFC will end. At the same time, you need to know that you need to contact the MFC that is located in the locality in which the marriage took place or in which one of the spouses is registered. For example, if the spouses got married in Rostov, then they need to contact the MFC of Rostov, and not the city in which they now live.
The sequence of actions for divorce through the MFC will be approximately as follows:
- Find out whether the divorce document is accepted at the MFC you need.
- Make an appointment in advance by phone or through State Services. This will help avoid queues.
- On the appointed day, come to the institution with prepared documents and take a receipt from the employee for payment of the state fee.
- Pay the state fee at the nearest bank branch.
- Fill out an application in form 9, 10 or 11 (the principles of selection are described in the article above).
- Submit the document to the MFC employee.
- Receive a receipt from him confirming the acceptance of the papers.
The same documents are submitted to the MFC as in the case of applying directly to the registry office - a divorce application signed by both spouses, passports of the husband and wife, a receipt for payment of the state fee. If the divorce is carried out unilaterally, then you need to prepare documentary evidence of the grounds. This may be a copy of the sentence of imprisonment, a certificate of recognition as incompetent, etc.
In a few days, the spouses will receive a notification about the need to visit the registry office for further divorce procedures. It will indicate the date and time of your visit, as well as the documents you need to take with you. Failure to appear at the registry office on the appointed date will result in the divorce not taking place. Former spouses also receive a divorce certificate at the registry office, and not at the MFC. In general, this method is not very convenient, and therefore is not very popular.
It is much more convenient to file for divorce through the State Services portal. This option is possible if the spouses have no children, property issues do not cause disagreements, and both parties agree to a divorce.
It’s not difficult to navigate the portal; our mini-instructions will help you with this:
- Log in to the portal using your username and password.
- Go to the ".
- Expand the “All services” list (will be at the bottom of the page) and select the “Registration of divorce by mutual consent” section.
Next, you will need to fill out all the fields of the electronic application and pay the state fee. You can do this directly on the portal, in which case you can get a discount of 200 rubles.
If this is not your first time using the State Services portal, then some data, for example, passport data, will already be automatically entered into the appropriate columns. Check them carefully, if any error has crept in, correct it. Do not forget to indicate the number and date of the registration, as well as the date of registration, this information is indicated in your marriage registration certificate. If after divorce a change of surname is required, add information about this in the appropriate column.
Don't forget to select the address of the registry office closest to you. You will need to appear there in person on the appointed date, together with your spouse, and provide the employee with the originals of the documents specified in the application. If the divorce occurs by mutual consent, then after filling out personal data you need to click the “Invite” button, after which the second spouse will continue filling out the document, but through his personal account.
When contacting the registry office, you will also need to fill out an application, the form of which can be obtained from the department.
Documents needed for divorce through the registry office:
- Passports.
- Marriage certificate.
- The court decision (if any) is in the original.
- Receipt for payment of state duty.
- If the husband or wife is declared incompetent, then you will need to take documents from the guardian.
According to the established procedure, during a divorce, a previously issued marriage certificate will need to be surrendered. In exchange, you and your ex-spouse will be issued a divorce certificate.
Divorce through court
If spouses have common minor children, there are property disputes, or someone does not want to get a divorce, they will have to act through the courts. You need to be prepared for a lengthy lawsuit that will consume some of your time and, possibly, money. However, in accordance with Article 21 of the RF IC, there is no other option.
You can start a divorce through the court only after filing a statement of claim. It is written on paper by hand or typed on a computer; some points can be drawn up in any form, but compliance with the norms of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation is mandatory. A properly drafted claim must contain the following information:
- In the header, in the upper right corner - the name of the court, its location, surname, first name and patronymic of the plaintiff and defendant, along with residential addresses. If possible, a telephone number is also indicated, possibly a mobile one.
- Information about the marriage - when it was concluded, who the second spouse was, whether there was a joint household, whether there were common children, until what time the spouses lived together.
- Are there any disputes related to the divorce - about the future fate of the children, the procedure for their financial support, the division of joint property. other moments.
- The essence of the statement of claim: only the dissolution of the marriage with the defendant or also the determination of the place of further residence of minor children, their financial support, division of property, determination of shares.
- Date of filing the statement of claim and signature of the plaintiff.
The statement of claim must contain references to legislative acts confirming the legality of the plaintiff’s claims and reflecting his position. The claim must also include a list of attached documents. The statement of claim should not contain personal emotions, errors, typos, strikeouts (corrections), and the wording should not be interpreted in two ways. If the claim is made with violations, it will be returned to you with an indication of the errors and you will have to start all over again.
If the parties do not have any disputes regarding the children, the property is divided by mutual agreement, or its value is estimated at less than 50,000 rubles, then the statement of claim is sent to the magistrate’s court at the defendant’s place of residence. In cases where the spouses cannot agree among themselves on the procedure for raising and maintaining children, or the property subject to division through the court is valued at an amount greater than 50,000 rubles, you need to contact the district court.
The statement of claim is sent to the court at the defendant’s place of residence. if its location cannot be determined or there are other grounds determined by law, then the claim may be sent to the court at the plaintiff’s place of residence. You can bring it along with the attached documents to the court office or send it by mail. You must be present at the trial and be prepared to provide the documents or evidence required by the court.
State duty on divorce
According to Art. 333.19 part 5 clause 1. Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the cost of the state fee when filing a statement of claim for divorce is 600 rubles. However, if the plaintiff also intends to ask for alimony payments or division of property, then the amount will be different. In the first case, you will have to pay an additional 150 rubles, and in the second, the cost of the state duty will be affected by the cost of the statement of claim. The minimum amount here will be 1,000 rubles, the maximum - 60,600 rubles.
The plaintiff must calculate the amount of the state fee himself, and then pay it using a receipt at any bank branch. To avoid problems, it is better to entrust the calculation to an experienced lawyer who will do everything correctly. If the amount of the state fee turns out to be too large for the plaintiff, you can file a request for an installment plan or deferment of payment. In this case, you need to be prepared to document your poor financial situation and the impossibility of paying the state duty in full immediately.
Changing your last name during divorce
After a divorce, you can apply to change your last name. This moment will not be difficult and will not cause problems. First you will need to fill out an application, which is sent to the passport office. in case of divorce through the State Services portal, the new surname can be entered in the appropriate column.
In each case, the procedure for changing a surname may have its own nuances. To avoid any difficulties, it is better to consult a lawyer on this issue, who will tell you how to act more correctly and will help you collect the necessary documents and draw up an application with you.
Divorce from a convicted person
The law provides for divorce if one of the spouses is sentenced to imprisonment. However, under a simplified procedure, when the consent of the serving spouse is not required, a divorce can be obtained only if the prison term is more than three years, otherwise one will have to divorce according to the main procedure.
When considering a claim for divorce, the judge will take into account the following points:
- spouse's term of imprisonment;
- potential danger on his part to members of his family;
- the financial condition of the plaintiff;
- the plaintiff has psychological or emotional problems;
- other points.
However, there is no need to indicate these reasons in the statement of claim; it is enough to attach a copy of the court verdict that has entered into legal force. In some situations, you can get a divorce even if there are minor children, and the defendant categorically disagrees with the divorce.
Divorce if one of the spouses is in another city
If one of the spouses is in another city, then there are no problems with divorce. The procedure is the same. as in the situations described above - through State Services, by submitting an application to the registry office or in court. If your spouse is in another country, it will be more difficult to get a divorce, we’ll talk about this below
Divorce with a missing person
In cases where the location of the spouse is unknown, divorce is possible in one of two scenarios. The first is relevant if the spouse is declared missing. in this case, the divorce occurs in the registry office, regardless of the existing joint minor children. If the spouse is not recognized as missing, the divorce occurs approximately in the following order:
- Submitting an application to recognize a spouse as missing. This is possible if there is no information about the person for a year, which is stated in Art. 42 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The document is submitted to the judicial authority at the place of residence of the interested person (Article 276 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation), the application must indicate the purposes of recognizing the citizen as missing and factors that could threaten his life or health (Article 277 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation)
- If the court, having considered the application, recognized the spouse as missing, then with the court’s decision you can contact the registry office, where the corresponding application is filled out. Along with it, the court decision, the spouse’s passport and the marriage certificate are submitted. The state duty is paid in the amount established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- 30 days after filing the application, you must visit the registry office and obtain a divorce certificate.
Also, the spouse interested in divorce is given back a marriage certificate with a note about its dissolution. This point is provided for in Art. 34 clause 3 of Law No. 143-FZ. This algorithm is possible if the spouse disappeared more than a year ago; in other cases, you will have to do things differently.
If less than a year has passed since the disappearance of the spouse, then the action for divorce can be to file a claim for divorce in the magistrate's court located at the last known place of residence of the spouse. In this case, there may be certain difficulties - the court is obliged to notify the defendant of the filed claim. In addition, a lawyer will be appointed to protect the interests of the defendant. If the court satisfies the claim, then you must contact the registry office with its decision and act in accordance with the general instructions.
How to get advice from a divorce lawyer
To avoid the serious consequences of divorce, not to lose property and to obtain joint custody, you need to seek advice from an experienced lawyer. He will analyze the situation and tell you which divorce strategy is best to choose. Professional lawyers provide advice on issues related to divorce:
- property disputes;
- conflicts related to shared custody and child support;
- unilateral divorce.
If you are asked to sign a settlement agreement, take your time. Use the services of our divorce lawyer, let him familiarize himself with the contents, perhaps a bad deal is being imposed on you. We will help maintain warm relationships within the family. If you have any doubts, contact our divorce lawyer by phone and get comprehensive information.