Legislative acts regulating the issue of receiving benefits for disabled pensioners
The main regulatory legal acts covering the problems of registering disability, medical examination and sanitary procedures for citizens, pensions or other additional payments, providing benefits and concessions for this category of citizens are:
- Federal law number 181-FZ (November 24, 1995);
- Resolution (order) of the Government of Russia No. 95 (February 20, 2006);
- Order of the Ministry of Health No. 317 (June 8, 2015);
- Order No. 17 of the Ministry of Labor (January 21, 2021);
- Resolution (order) of the Government of Russia number 74 (January 26, 2021).
They include, among other things:
- What benefits are available to disabled pensioners?
- The procedure for assigning disability is determined;
- A list of diseases and injuries is provided, the receipt of which is the reason for receiving the group (first, second, third, disabled since childhood);
- The procedure for receiving a referral and collecting certificates and documents for undergoing a medical and social examination is regulated, and the period and timing of the examination are described.
Legislative framework for assigning tax benefits to people with disabilities
To improve the quality of life of people with serious pathologies and compensate for the associated inconveniences, a number of legal acts have been developed:
| Title, date of adoption, document number | Positions of Interest |
| Federal Law “On Social Protection of Disabled Persons in the Russian Federation” dated November 24, 1995 N 181-FZ | A list of preferences for people with different disability groups is outlined |
| Federal Law “On Ratification of the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities” dated 05/03/2012 N 46-FZ | Announces the entry into force in Russia of the international bill of rights for people with disabilities |
| “Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Part One)” dated July 31, 1998 N 146-FZ | A document with a complete list of grounds for levying taxes and providing tax benefits for different categories of citizens of the Russian Federation |
| Presidential Decree “On additional measures of social protection of people with disabilities” dated October 20, 1992 N 1157 | Obliges the government to provide full access to government services and provide assistance in finding work for people with disabilities |
| Federal Law “On Insurance Pensions” dated December 28, 2013 N 400-FZ | Based on this document, pensions are assigned to different categories of disabled people. |
What do disabled pensioners get paid every month in 2021?
The only type of federal support for disabled people is a pension. But there are also other mandatory benefits provided by the state every month.
The list of all types of compensation paid to help such citizens is as follows:
- Monthly Cash Payment (M.M.V.);
- Social pension provision;
- Additional Monthly Material Support (D.E.M.O);
- Set of Social Services (S.S.U, is part of E.D.V);
- Federal Social Additional Payment (F.S.D);
- Payments provided to care for a pensioner;
- Pensions due to disability (labor or insurance);
- Benefits due to industrial injury or damage during military service;
- Monetary compensation made after payment for housing and communal services, telephone communications, travel (all types of urban public, as well as intercity transport).
For reference! In 2021, they planned to index the amounts of some compensation. On April 1, 2018, the amount of the social pension increased, and on February 1, 2018, the monthly payment increased.
According to the new program of the Russian government, benefits should exceed inflation. In 2021, they were indexed by 4.1%, while the inflation rate was 4%. Taking this into account, the real increase in the amount of additional payments is 0.1 percent.
Social pensions have increased:
- For persons with disability group number 1, the increase was 412 rubles;
- Citizens in the second group will receive an additional 206 rubles;
- For persons with group 3 disabilities, payments were increased by 175 rubles.
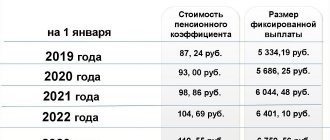
What are the pension amounts for disabled people of different groups?
| Disability group | Pension amount |
| First; second (from childhood) | RUB 10,360 52 kopecks |
| Second | RUB 5,180 24 kopecks |
| Third | RUR 4,403 24 kopecks |
| The first (from childhood); disabled children | RUB 12,432 44 kopecks |
If a citizen refuses to receive benefits, he/she receives the right to monthly compensation:
Features of providing cash payments
Based on the provisions of the legislation of the Russian Federation, a disabled citizen has the right not only to benefits, but also to monetary compensation. She may be:
1) Social pension.
All non-working disabled people receive this payment. The amount is not very large, but it is strictly fixed. As practice shows, every year the Government indexes this amount. In 2018, this amount will look like this:
| From 04/10/2017 | From 01.04.2018 | |
| Disabled people 2nd group | 5109.25 rubles | According to the draft budget, the indexation percentage is assumed to be based on the inflation rate (according to preliminary forecasts, 4.1%) |
| Disabled people since childhood, 2 groups | 10217.53 rubles |
2) Insurance pension.
If before becoming disabled, a citizen worked or was already working as a disabled person, he has the right to receive an insurance pension. Its amount is affected by the accrued salary. A formal insurance period (from 1 day) is also sufficient. The pension is paid with an additional bonus - a fixed payment.
3) It is also possible to accrue monthly cash payments.
This benefit is considered additional. The establishment of its value, as well as its payment, is carried out by the Pension Fund bodies. The amount is subject to revision once a year. It includes the cash payment itself and certain social services (for example, a discount on travel on long-distance trains, a voucher to a boarding house, and so on). The EDV was introduced in 2005 to monetize preferences:
| EDV | including NSO | |
| 2017 | 2527,06 | 1048,97 |
| 2018 | According to the draft budget, the indexation percentage should be 3.2% | |
4) If there are dependents, the insurance pension can be paid along with an additional payment.
Full list of benefits, their characteristics
Benefits for disabled pensioners cover many areas of life. Among them:
- Housing preferences;
- Benefits related to personal transport;
- Social assistance in purchasing medicines or other medical goods;
- Travel benefits (city public transport, intercity communication);
- Sanatorium treatment service;
- Tax;
- Special working conditions for working pensioners;
- In the field of education;
- Help with social adaptation.
In the field of housing services
How are benefits processed?
To apply for benefits, a disabled person must contact the social protection office at their place of residence. Also, when applying for various types of benefits, you may need to visit the traffic police, tax office, housing and communal services and the MFC.
Package of documents for registration of benefits
When receiving benefits, you will need the following package of documents:
- A document that identifies the person applying and confirms Russian citizenship;
- Registration;
- Papers required to pay utility bills;
- Certificate of completion of a medical and social examination, which confirms the citizen’s disability group (other certificates may be needed);
- Pensioner ID;
- SNILS;
- Documents for personal vehicles;
- Certificate of income;
- Documents confirming the status of a combat veteran;
- Paper about the composition of the family, the presence of dependents;
- Documents that confirm a person’s right to a certain living space.
If necessary, the disabled person or the person caring for him will be asked to bring additional papers to confirm the data.
Procedure for receiving payments and benefits
All submitted documents are reviewed within 30 days. Starting from the next calendar month, a pension or other payments begin to be credited to the person’s bank card. If this is not available, a citizen can contact a Russian Post office or use the services of special companies.
When applying for tax benefits, preferences begin to apply from the moment the next tax calculation is made by the inspectorate.
Benefits for individual entrepreneurs with disabilities
Many disabled people prefer to continue working and become individual entrepreneurs. It is important for them to understand what benefits they can claim in this case. 2019 does not bring any changes in this case.
Special conditions for disabled people of any degree are not provided when opening an individual entrepreneur. Further, depending on the chosen taxation system, various privileges apply.
For example, an individual entrepreneur with a disability can pay for a patent with a 30% discount. This is a very profitable option for starting a business.
The simplified system offers benefits at the regional level. They consist of reducing the payment of income tax by 1%.
Under the general system, a disabled individual entrepreneur does not have to pay VAT. However, this only applies to those whose revenue for 3 months was less than 2 million rubles.
According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, disabled people of the 1st and 2nd degrees are entitled to income tax privileges. Thus, they are entitled to a tax deduction from personal income tax amounting to 500 rubles for each calendar month.
All these concessions help special individual entrepreneurs to start and conduct activities in one area or another.
What regional benefits exist and where can you find out about them?
There are different types of regional benefits (for example, transport or housing). Information about them can be obtained from local branches of the social protection bureau and departments for working with the disabled. There are special targeted regional programs for these needs.
In Moscow, a regional type of benefit is the issuance of a “Muscovite social card” to a disabled person, which, for example, allows free travel on city public transport.
In St. Petersburg, a person with disabilities can count on discounted travel with comfortable service (10 percent of the full cost) to such institutions as:
- Hospitals;
- Clinics;
- Executive authorities, etc.
In some cities of Russia (Ufa, Novosibirsk, Nizhny Novgorod) there are certain coefficients for calculating the EDV, which is why the amount of payments differs from those in other subjects of the state.
What benefits do disabled people have regarding tax payments?
1.
Disabled people of the first and second groups are exempt from property tax if they inherited real estate.
2.
Disabled people of the second and first groups, disabled children, disabled WWII, who have land plots registered before 2004, have the following deduction: the tax base for calculating the tax (land price) is reduced by 10,000 rubles.
3.
Transport benefits for disabled people consist of a 50% tax discount when purchasing a car through social security authorities (power up to 100 hp) and complete tax exemption in case of owning a car that has been specially converted for a person with disabilities.
Benefits in the form of tax deductions
- Every month, 500 rubles are deducted from the personal income tax base for disabled people of the second and first groups and disabled children.
- The monthly tax deduction for parents (trustees, guardians, spouses, adoptive parents) of minor children who are disabled is 3,000 rubles. The same amount for disabled children under 24 years of age who are students (students, interns, graduate students);
- 3,000 rubles is a monthly tax deduction for disabled people who are liquidators of the Chernobyl accident, victims of the Mayak production association (the accident happened in 1957) or former military personnel who received disability due to injury.
Monetization of benefits
Disabled people only recently received the right to monetize various types of benefits. Federal Law No. 178 states that compensation in the form of cash payments can be received for:
- Purchasing medicines;
- Treatment in sanatoriums;
- Use of transport.
The possibility of compensation for payment of housing and communal services is separately prescribed, but this function is not included in the established list.
The total amount of all possible payments (for all 3 types of benefits in the above list) is equal to 930 rubles 12 kopecks. Of them:
- 716 rub. 40 kopecks – funds for the purchase of medicines;
- 102 rubles 89 kopecks – provision of preferential travel;
- 110 rub. 83 kopecks – payments for treatment in sanatoriums.
To monetize, a person must write a refusal of the benefits provided in favor of payments in writing. The application is submitted to the branch of the Russian Pension Fund. The funds will be transferred to the disabled person’s specified bank account or through Russian Post.
The service of providing monetary compensation in lieu of benefits can only be beneficial if the disabled person does not require all or any of them.
Thematic video with more detailed information regarding the monetization of benefits:
Retired people are entitled to an extensive list of benefits, preferences and monetary compensation in many areas of life. The state supports such pensioners, including providing them with medicines and sanatorium treatment, and makes it possible to significantly reduce the cost of transport, both public and personal.
Labor benefits
Disabled people are entitled to a whole range of employment benefits at their place of work:
- Shortened work week: no more than 35 hours compared to the standard 40 hours. In this case, the shortened week is paid to the disabled person in full if he had worked all 40 hours (Article 92 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The IPR may indicate a different duration of work recommended for a disabled person.
- Involvement in overtime work, work on weekends or at night is permitted only with the consent of the disabled person himself (Article 96, 113 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Extended leave: 30 days instead of the standard 28 days (Article 23 of the Law on Persons with Disabilities).
- The right to leave without pay for 60 days (Article 128 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). An employer cannot refuse additional leave to a disabled person.
The employer can set out additional guarantees and benefits in local documents.